Anova Interpretation
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) can determine whether the means of three or more groups are different ANOVA uses Ftests to statistically test the equality of means In this post, I’ll show you how ANOVA and Ftests work using a oneway ANOVA example.
Anova interpretation. ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) in Excel is the single and twofactor method which is used to perform the null hypothesis test which says if the test will be PASSED for Null Hypothesis if from all the population values are exactly equal to each other If any or at least one value is different from other values, then the null hypothesis will be FAlLED. ANOVA determines whether the groups created by the levels of the independent variable are statistically different by calculating whether the means of the treatment levels are different from the overall mean of the dependent variable If any of the group means is significantly different from the overall mean, then the null hypothesis is rejected. The twoway ANOVA compares the mean differences between groups that have been split on two independent variables (called factors) The primary purpose of a twoway ANOVA is to understand if there.
Interpretation of ANOVA test If the null hypothesis of equal category means is not rejected, then the independent variable doesn’t have a significant effect on the dependent variable On the other hand, if the null hypothesis is rejected, the effect of the independent variable is significant. Rosenthal & Rosnow, 1991;. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) can determine whether the means of three or more groups are different ANOVA uses Ftests to statistically test the equality of means In this post, I’ll show you how ANOVA and Ftests work using a oneway ANOVA example.
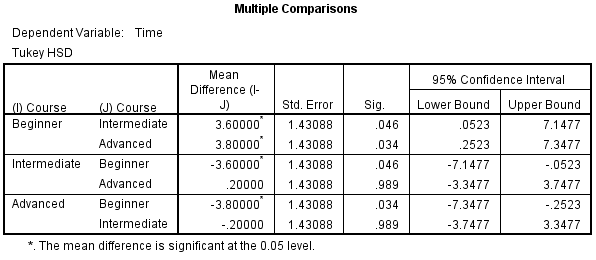
Interaction Effects in ANOVA 1 Interaction Effects in ANOVA This handout is designed to provide some background and information on the analysis and interpretation of interaction effects in the Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) This is a complex topic and the handout is necessarily incomplete In practice, be sure to consult the text and other references on ANOVA (Kirk, 19;. B) The posthoc analysis of ANOVA will be appropriate During ANOVA, only ONE pair of data is analyzed at a time, which means that the pvalue has to be corrected for the multiple possible comparisons The posthoc analysis of ANOVA takes this correction into account The Tukey test compares every mean with every other mean. In the Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), we use the statistical analysis to test the degree of differences between two or more groups in an experiment besides, we use the ANOVA table to display the results in tabular form And this data is used to test the test hypotheses about the population mean.
ANOVA is short for AN alysis O f VA riance The main purpose of an ANOVA is to test if two or more groups differ from each other significantly in one or more characteristics. Then I made oneway ANOVA analysis, Here comes the questions 2A and 3A are significantly higher than 1A in the first chart, however, no significant differences are observed for 1B, 2B and 3B in. Interpretation of the ANOVA table The test statistic is the \(F\) value of 959 Using an \(\alpha\) of 005, we have \(F_{005;.
To study more than two populations at once, we need different types of statistical tools Analysis of variance, or ANOVA, is a technique from statistical interference that allows us to deal with several populations. ANOVA partitions the variability among all the values into one component that is due to variability among group means (due to the treatment) and another component that is due to variability within the groups (also called residual variation). Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Analysis of variance (ANOVA) refers to a broad class of methods for studying variations among samples under di erent conditions (or treatments) The simplest form of ANOVA can be used for testing three or more population means It can be considered as an extension of the twosample ttests we discussed for comparing two population means.
1 Statistical Analysis 8 Twoway analysis of variance (ANOVA) Research question type Explaining a continuous variable with 2 categorical variables What kind of variables?. OneWay Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Example Problem Introduction Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a hypothesistesting technique used to test the equality of two or more population (or treatment) means by examining the variances of samples that are taken ANOVA allows one to determine whether the differences between the samples are simply due to random error (sampling errors) or whether there are systematic treatment effects that causes the mean in one group to differ from the mean in another. ANCOVA basically combines ANOVA and regression This tutorial walks you through the analysis with an example in SPSS Read more.
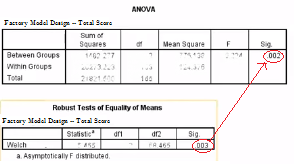
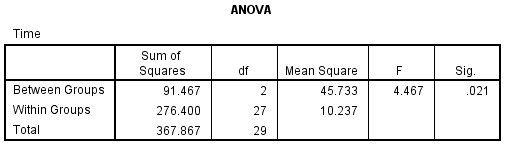
INTERPRETING THE ONEWAY ANOVA PAGE 2 The third table from the ANOVA output, (ANOVA) is the key table because it shows whether the overall F ratio for the ANOVA is significant Note that our F ratio (6414) is significant (p = 001) at the 05 alpha level When reporting this finding – we would write, for example, F(3, 36) = 641, p < 01 The F indicates that we are using an F test (ie. \, 2, \, 12}\) = 3 (see the F distribution table in Chapter 1) Since the test statistic is much larger than the critical value, we reject the null hypothesis of equal population means and conclude that there is a (statistically) significant difference among the population means. This video is about Interpretting the ANOVA Results Table.
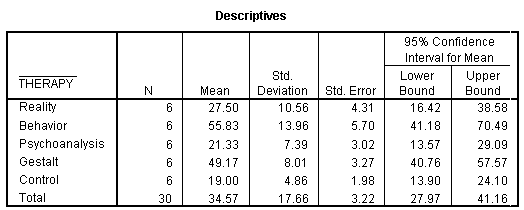
Interpretation Look in the standard deviation (StDev) column of the oneway ANOVA output to determine whether the standard deviations are approximately equal If you cannot assume equal variances, use Welch's ANOVA, which is an option for oneway ANOVA that is available in Minitab Statistical Software. Interpreting the OneWay ANOVA Results The Summary table indicates that the mean strengths range from a low of for supplier 4 to a high of for supplier 1 Our sample means are different However, we need to determine whether our data support the notion that the population means are not equal. Running head ANOVA DATA ANALYSIS AND APPLICATION normally distributed, and there will be a homogeneity of variance As the independence of observations is determined methodologically, it is not necessary to test it Located above is the SPSS histogram output for Section 1 and quiz 3, Section 2 and quiz 3 and Section 3 and quiz 3 The frequency of the data shows the data values in each group.
The ANOVA procedure performs analysis of variance (ANOVA) for balanced data from a wide variety of experimental designs In analysis of variance, a continuous response variable, known as a dependent variable, is measured under experimental conditions identified by classification variables, known as independent variables. ANOVA stands for ‘Analysis of Variance’ It actually means analysis of variation in means of different groups of a population or different populations It is an advanced version of t – test While ttest is used to compare two means, ANOVA can be used for more than two means It studies whether the variation betw. A single factor or oneway ANOVA is used to test the null hypothesis that the means of several populations are all equal Below you can find the salaries of people who have a degree in economics, medicine or history H 1 at least one of the means is different.
Then I made oneway ANOVA analysis, Here comes the questions 2A and 3A are significantly higher than 1A in the first chart, however, no significant differences are observed for 1B, 2B and 3B in. Analysis Of Variance The Analysis Of Variance, popularly known as the ANOVA, can be used in cases where there are more than two groups. ANalysis Of VAriance, written as ANOVA for short, is a statistical technique that compares sample populations based on their means and spread of the data The model helps us answer the question of whether the means of two or more groups are significantly different.
Null hypothesis – All means are equal Factor level – Each Factor can have multiple levels like Heavy, Medium and Low are three levels of Sales promotion ANOVA is used as a test of means for two or more populations The null hypothesis, typically is that all means are equal as you can see in the above example. ANOVA stands for Analysis Of Variance ANOVA was founded by Ronald Fisher in the year 1918 The name Analysis Of Variance was derived based on the approach in which the method uses the variance to determine the means whether they are different or equal It is a statistical method used to test the differences between two or more means. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a statistical technique that is used to check if the means of two or more groups are significantly different from each other ANOVA checks the impact of one or more factors by comparing the means of different samples.
Running head ANOVA DATA ANALYSIS AND APPLICATION normally distributed, and there will be a homogeneity of variance As the independence of observations is determined methodologically, it is not necessary to test it Located above is the SPSS histogram output for Section 1 and quiz 3, Section 2 and quiz 3 and Section 3 and quiz 3 The frequency of the data shows the data values in each group. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a statistical analysis tool that separates the total variability found within a data set into two components random and systematic factors. B) The posthoc analysis of ANOVA will be appropriate During ANOVA, only ONE pair of data is analyzed at a time, which means that the pvalue has to be corrected for the multiple possible comparisons The posthoc analysis of ANOVA takes this correction into account The Tukey test compares every mean with every other mean.
INTERPRETING THE ONEWAY ANOVA PAGE 2 The third table from the ANOVA output, (ANOVA) is the key table because it shows whether the overall Fratio for the ANOVA is significant Note that our Fratio (6414) is significant (p=001) at the05 alpha level When reporting this finding – we would write, for example, F(3, 36) = 641, p. Continuous (scale/interval/ratio) and 2 independent categorical variables (factors) Common Applications Comparing means of a single variable at different levels of two conditions (factors) in scientific experiments. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures (such as the "variation" among and between groups) used to analyze the differences among group means in a sampleANOVA was developed by the statistician Ronald FisherThe ANOVA is based on the law of total variance, where the observed variance in a particular variable is partitioned.
ANOVA short for “analysis of variance” is a statistical technique for testing if 3 () population means are all equal The two simplest scenarios are oneway ANOVA for comparing 3 () groups on 1 variable do all children from school A, B and C have equal mean IQ scores?. Interpretation Look in the standard deviation (StDev) column of the oneway ANOVA output to determine whether the standard deviations are approximately equal If you cannot assume equal variances, use Welch's ANOVA, which is an option for oneway ANOVA that is available in Minitab Statistical Software. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) uses Ftests to statistically assess the equality of means when you have three or more groups In this post, I’ll answer several common questions about the Ftest How do Ftests work?.
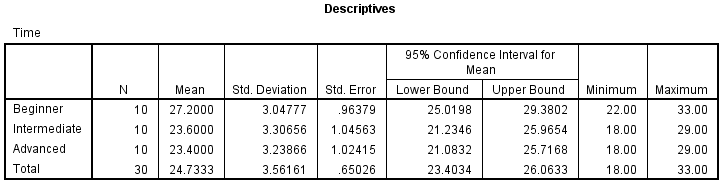
OneWay Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and Multiple Comparisons For this example, we return to the population density of huntergatherers in three different forest ecosystems (data taken from Binford 00) We have three ecosystems (s= 3), each with a sample size of ten huntergatherer groups (n= 10) For this problem we are interested in whether there is a significant difference between the mean group sizes across the three ecosystems, and if so, what is the underlying pattern of variation. For a complete explanation of the output you have to interpret when checking your data for the six assumptions required to carry out a oneway ANOVA, see our Features Oneway ANOVA page This includes relevant boxplots, and output from the ShapiroWilk test for normality and test for homogeneity of variances. Ashley Crossman Updated December 31, 18 Analysis of Variance, or ANOVA for short, is a statistical test that looks for significant differences between means on a particular measure For example, say you are interested in studying the education level of athletes in a community, so you survey people on various teams.
B) The posthoc analysis of ANOVA will be appropriate During ANOVA, only ONE pair of data is analyzed at a time, which means that the pvalue has to be corrected for the multiple possible comparisons The posthoc analysis of ANOVA takes this correction into account The Tukey test compares every mean with every other mean. Complete the following steps to interpret a oneway ANOVA Key output includes the pvalue, graphs of groups, group comparisons, R 2, and residual plots. B) The posthoc analysis of ANOVA will be appropriate During ANOVA, only ONE pair of data is analyzed at a time, which means that the pvalue has to be corrected for the multiple possible comparisons The posthoc analysis of ANOVA takes this correction into account The Tukey test compares every mean with every other mean.
ANOVA design, the term factor is a synonym of independent variable Therefore, “Type of Smile” is the factor in this experiment Since four types of smiles were compared, the factor “Type of Smile” has four levels An ANOVA conducted on a design in which there is only one factor is called a oneway ANOVA If an experiment has two factors, then the ANOVA is called a. To answer this question, ANOVA calculates a parameter called F statistics, which compares the variation among sample means (among different continents in our case) to the variation within groups (within continents) F statistics = Variation among sample means / Variation within groups. It describes the extent to which the scores differ from each other It is defined as the mean of the squared deviation of individual scores taken from the mean where x = X – M or deviation of the score from the mean, ie, variance = square of SD or, variance = σ 2 so σ =.
ANOVA statistically tests the differences between three or more group means For example, if you have three different teaching methods and you want to evaluate the average scores for these groups, you can use ANOVA However, ANOVA does have a drawback It can assess only one dependent variable at a time. A single factor or oneway ANOVA is used to test the null hypothesis that the means of several populations are all equal Below you can find the salaries of people who have a degree in economics, medicine or history H 0 μ 1 = μ 2 = μ 3 H 1 at least one of the means is different. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is an analysis tool used in statistics that splits an observed aggregate variability found inside a data set into two parts systematic factors and random factors The.
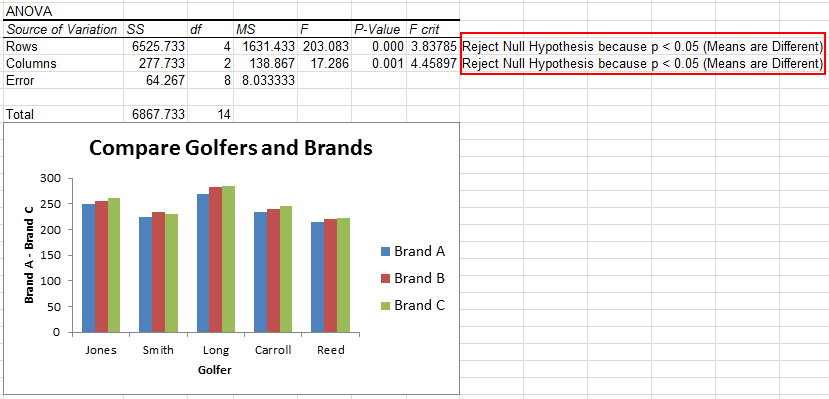
Analysis of variance, or ANOVA, is a linear modeling method for evaluating the relationship among fields For key drivers and for insights that are related to a number of charts, ANOVA tests whether the mean target value varies across categories of one input or combinations of categories of two inputs To test if the means are different, an ANOVA test compares the explained variance (caused by the input fields) to the unexplained variance (caused by the error source). So just eyeballing it, we can see that there are more words remembered in the Sugar condition We need our ANOVA to determine if the differences between condition means are significant We need ANOVA to make a conclusion about whether the IV (sugar amount) had an effect on the DV (number of words remembered). So just eyeballing it, we can see that there are more words remembered in the Sugar condition We need our ANOVA to determine if the differences between condition means are significant We need ANOVA to make a conclusion about whether the IV (sugar amount) had an effect on the DV (number of words remembered).
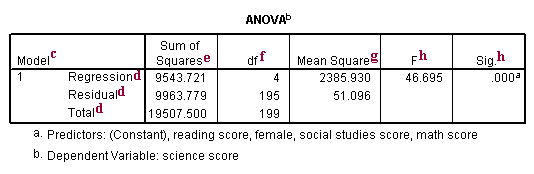
Continuous (scale/interval/ratio) and 2 independent categorical variables (factors) Common Applications Comparing means of a single variable at different levels of two conditions (factors) in scientific experiments. The hypothesis is based on available information and the investigator's belief about the population parameters The specific test considered here is called analysis of variance (ANOVA) and is a test of hypothesis that is appropriate to compare means of a continuous variable in two or more independent comparison groups. For statistical analyses, Regression Analysis and stepwise Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) are used Our results show that there is a significant negative impact of the project size and work effort.
ANOVA partitions the variability among all the values into one component that is due to variability among group means (due to the treatment) and another component that is due to variability within the groups (also called residual variation). The Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) has many varieties, but in essence, it has the purpose of evaluating whether factors are associated with any outcome values And factors are categorical variables. Why do we analyze variances to test means?.
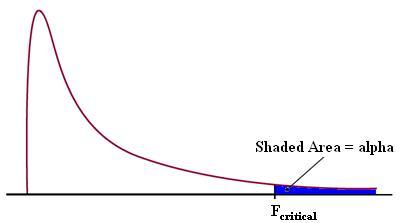
Winer, Brown, & Michels, 1991) for additional information. The ANOVA table also shows the statistics used to test hypotheses about the population means When the null hypothesis of equal means is true, the two mean squares estimate the same quantity (error variance), and should be of approximately equal magnitude In other words, their ratio should be close to 1. To deal with situations in which we need to make multiple comparisons we use ANOVA This test allows us to consider the parameters of several populations at once, without getting into some of the problems that confront us by conducting hypothesis tests on two parameters at a time.
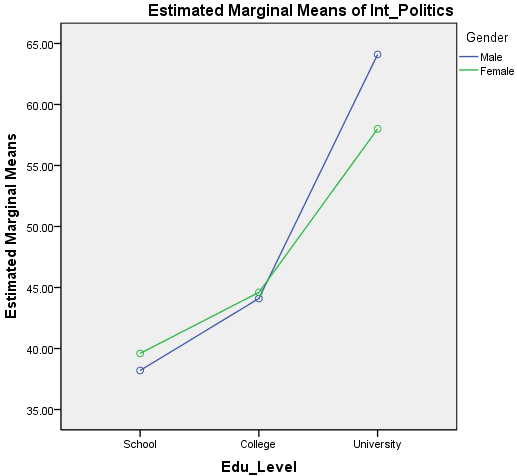
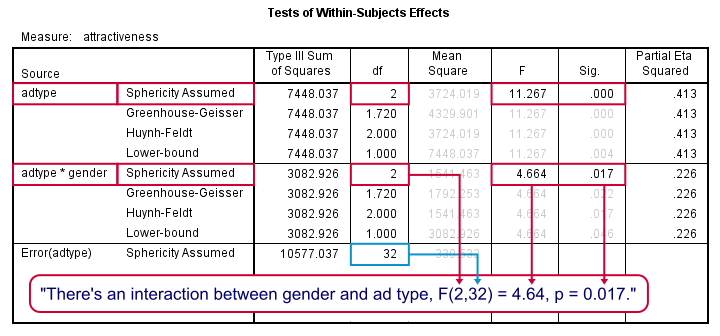
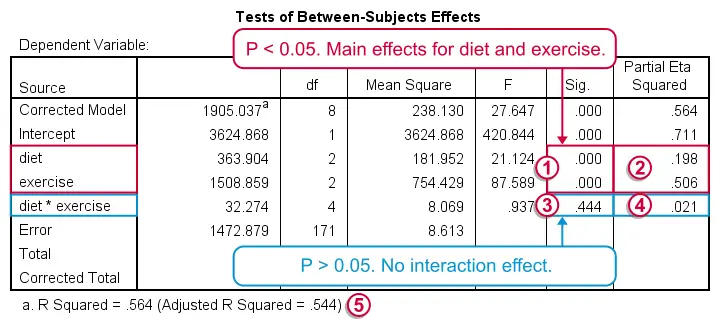
In ANOVA and regression, an interaction effect means that some effect depends on another variable Example women become happier but men become un happier if they have children So the effect of having children depends on sex. Interpretation of the ANOVA table is as follows In the ANOVA table, If the obtained Pvalue is less than or equivalent to the significance level, then the null hypothesis gets automatically rejected and concluded that all the means are not equal to the given population Analysis of Variance Repeated Measures. A description of the concepts behind Analysis of Variance There is an interactive visualization here http//demonstrationswolframcom/VisualANOVA/ but I h.
Two Way Anova Test Without Replication In Excel Two Factor
Two Way Anova Output And Interpretation In Spss Statistics Including Simple Main Effects Laerd Statistics
Spss Repeated Measures Anova Tutorial Ii
Anova Interpretation のギャラリー
Q Tbn And9gcq4uwhooi5eqjqucua5xz61flphszt5 Cvenhunk1ihuu5ybl9i Usqp Cau
Analysis Of Variance Anova
Welch S Anova Definition Assumptions Statistics How To

How Do I Interpret Data In Spss For A 1 Way Within Subjects Anova
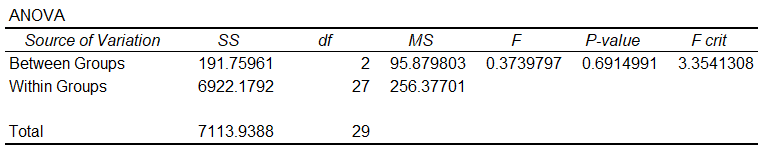
Perform A One Way Analysis Of Variance Anova In Excel By Dobromir Dikov Fcca Magnimetrics Medium
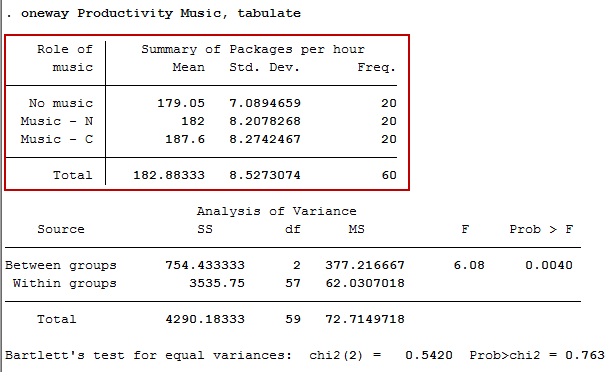
One Way Anova In Stata Procedure Output And Interpretation Of The Output Using A Relevant Example

14 3 Interpreting The Output

Help Online Origin Help One Two And Three Way Anova
One Way Anova In Spss Including Interpretation Easy Tutorial
Regression Analysis Spss Annotated Output
One Way Anova In Spss Statistics Understanding And Reporting The Output
One Way Anova Test In R Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
Tutorial 9 6a Factorial Anova
One Way Anova In Spss Including Interpretation Easy Tutorial
Two Way Anova Output And Interpretation In Spss Statistics Including Simple Main Effects Laerd Statistics
F Statistic F Value Definition And How To Run An F Test
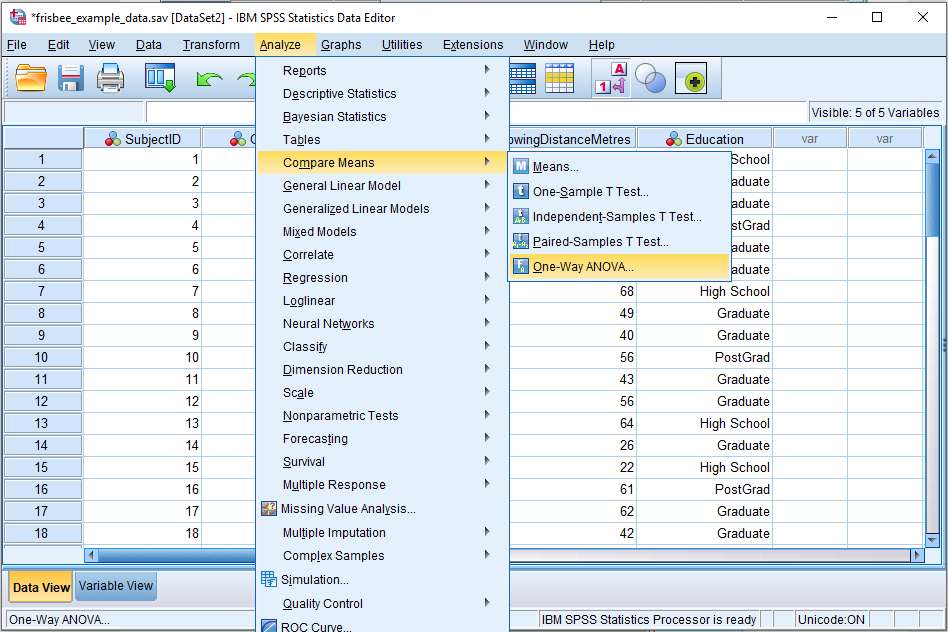
One Way Anova In Spss Including Interpretation Easy Tutorial
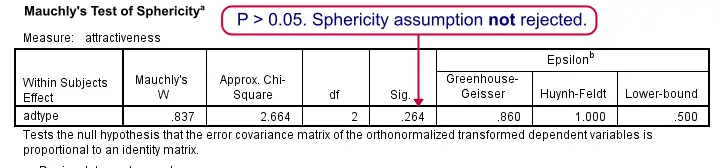
Spss Repeated Measures Anova Tutorial Ii

Hypothesis Testing Analysis Of Variance Anova

Interpret The Key Results For One Way Anova Minitab Express

14 3 Interpreting The Output

Understanding Anova By Looking At Your Household Budget
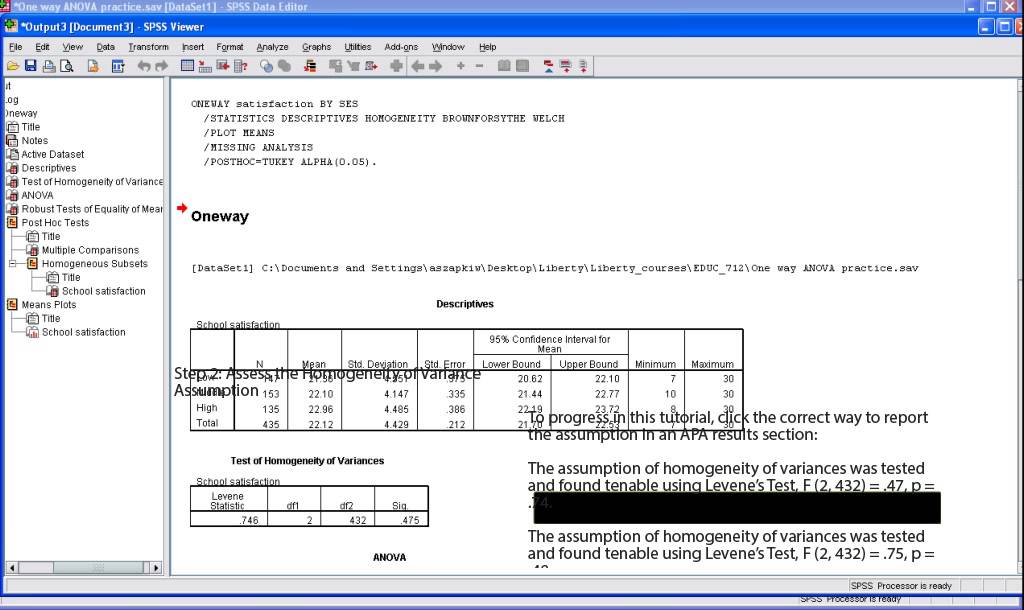
Spss Tutorial One Way Anova Youtube

Effect Size For Analysis Of Variance Anova Psycho Hawks

Confidence Interval For Anova Real Statistics Using Excelreal Statistics Using Excel

Interpret All Statistics And Graphs For One Way Anova Minitab Express

Anova Confidence Interval Interpretation Mathematics Stack Exchange
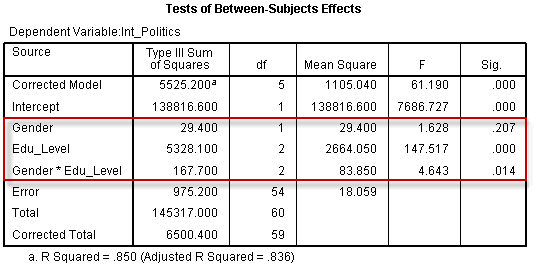
Two Way Anova Output And Interpretation In Spss Statistics Including Simple Main Effects Laerd Statistics

Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial

How To Interpret Anova Output When Comparing Two Nested Mixed Effect Models Cross Validated

Ppt Analysis And Interpretation Analysis Of Variance Anova Powerpoint Presentation Id
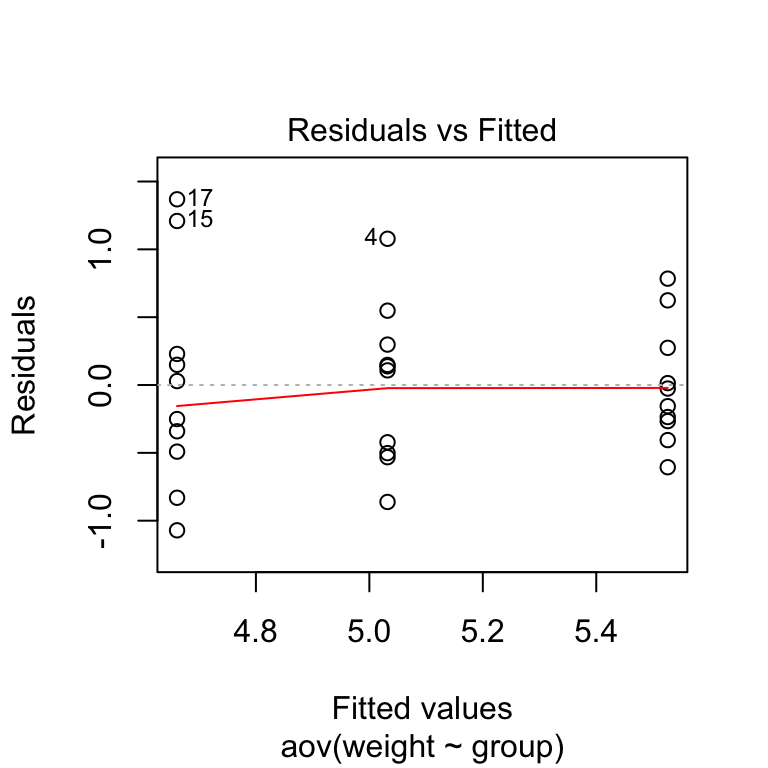
One Way Anova Test In R Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
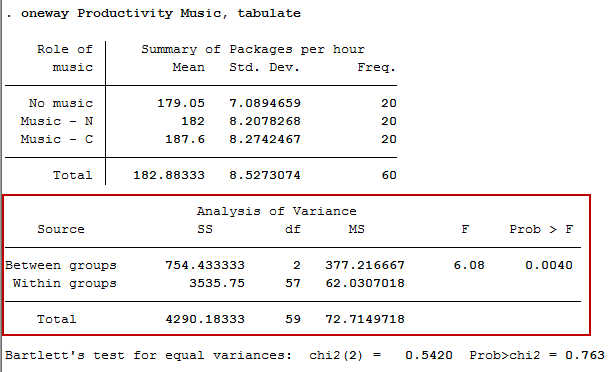
One Way Anova In Stata Procedure Output And Interpretation Of The Output Using A Relevant Example
Q Tbn And9gcsz5vlzpth6jd3th9c7y Zxt5bhl3zzky6zt5794tzk2zvim04b Usqp Cau
Repeated Measures Anova In Spss Including Interpretation Easy Spss Tutorial

Interpreting The Anova Results Table Youtube
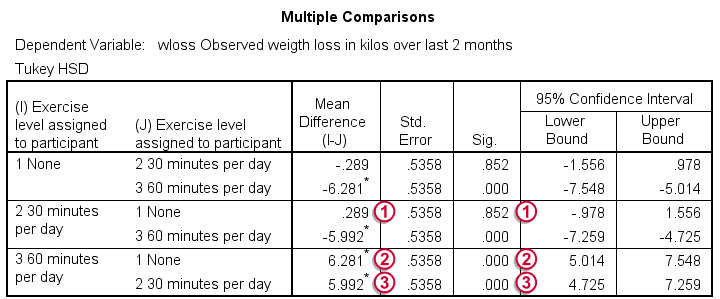
Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial

How Do I Report A 1 Way Between Subjects Anova In Apa Style
1
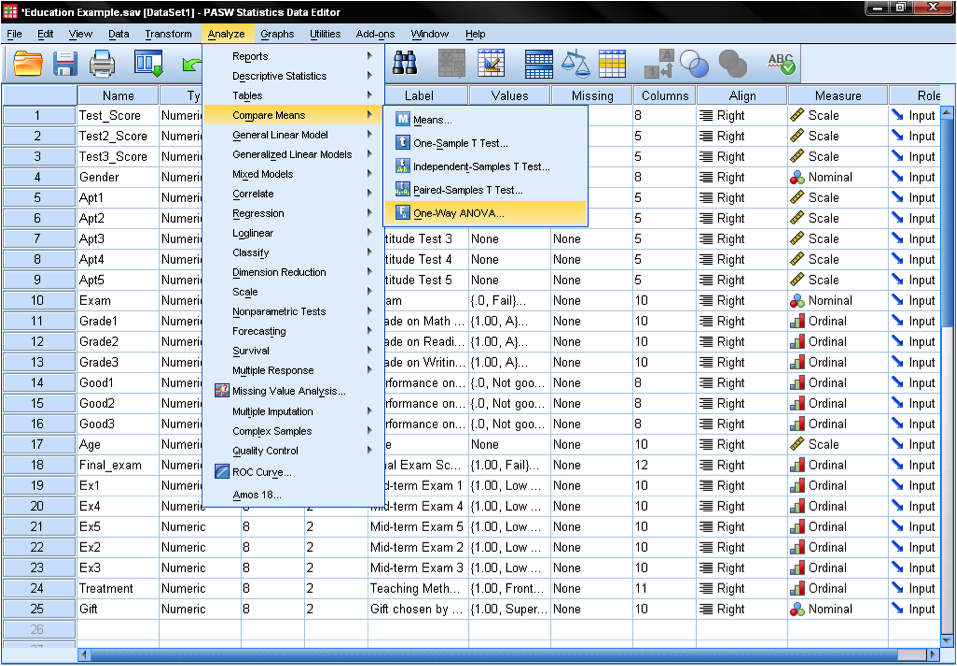
Conduct And Interpret A One Way Anova Statistics Solutions

How Do I Interpret Data In Spss For A 1 Way Between Subjects Anova

Perform A One Way Analysis Of Variance Anova In Excel Magnimetrics
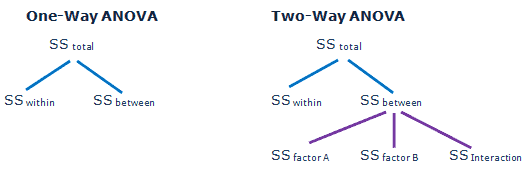
Anova Analysis Of Variation Six Sigma Study Guide
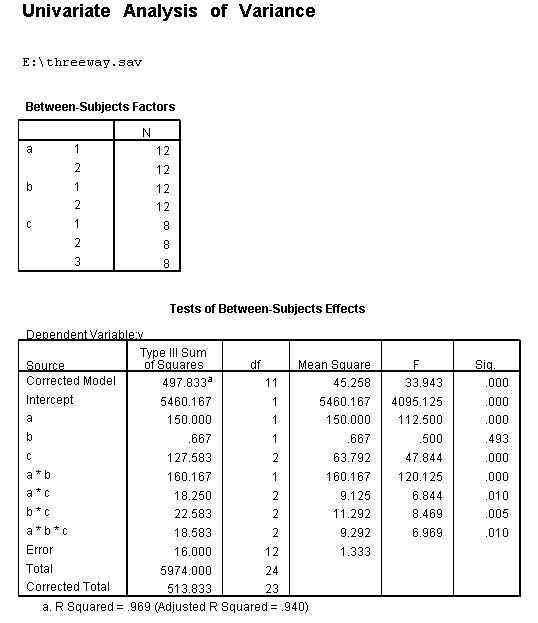
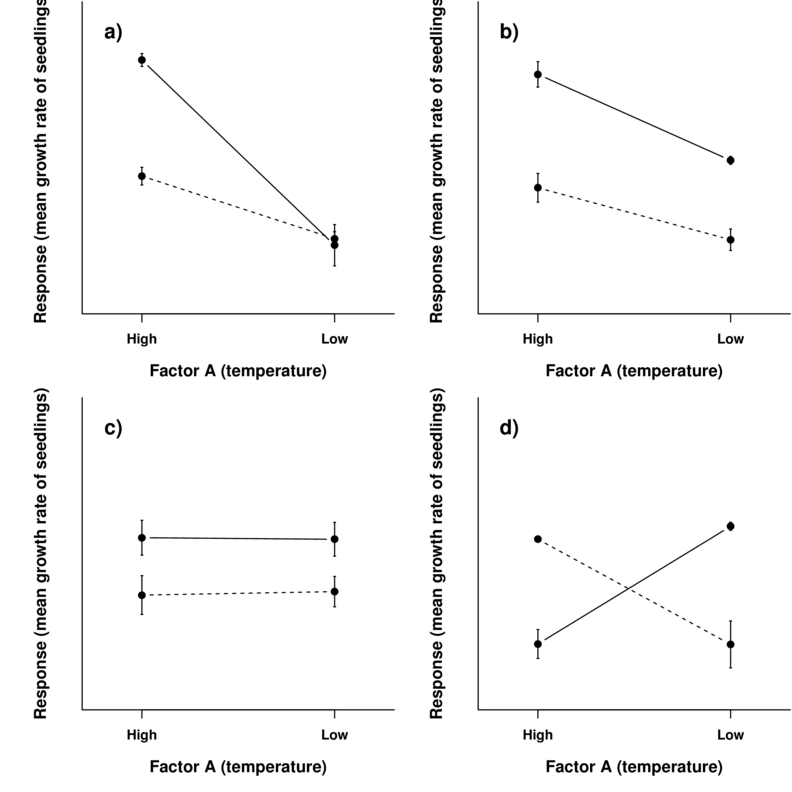
How Can I Explain A Three Way Interaction In Anova Spss Faq

Two Way Anova In Excel Two Factor Anova With Replication

One Way Anova In Spss Statistics Understanding And Reporting The Output

Two Way Anova Overview Spss Interpretation

Multi Factor Anova Interpretation Download Table
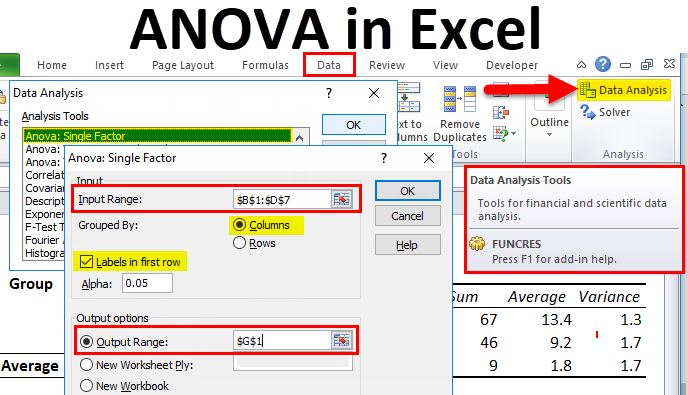
Anova In Excel Examples How To Use Excel Anova

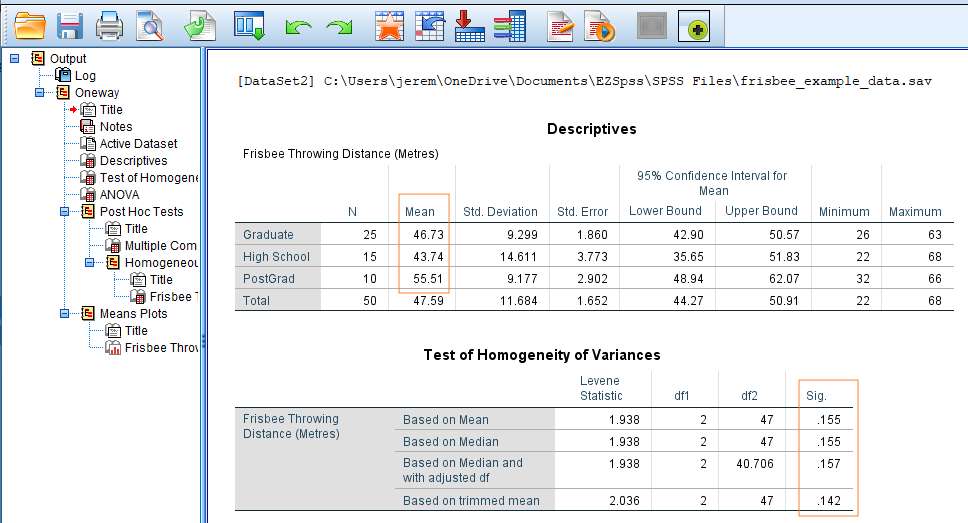
Spss Output Compare Means One Way Anova

How Do I Report A 1 Way Between Subjects Anova In Apa Style
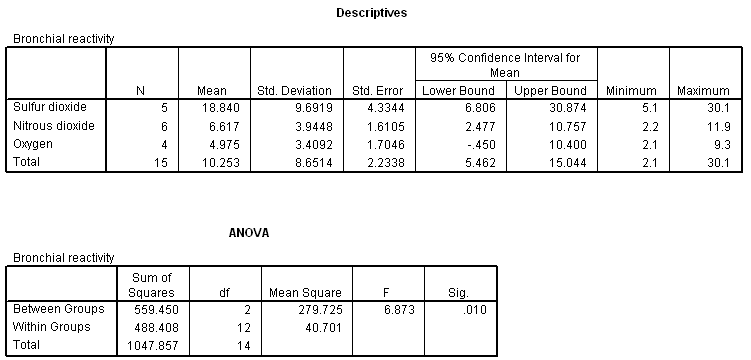
13 Anova Part B 2 07 Post Hoc Comparisons Kruskal Wallis Levene Procedures Review Questions True Or False In Rejecting An Anova Null Hypothesis You Are Saying There Is A Significant Difference Between All Groups List Methods To Compare
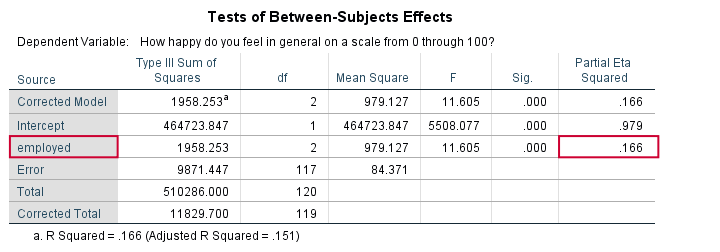
How To Get Partial Eta Squared From Spss
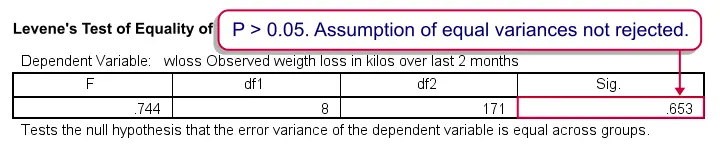
Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial
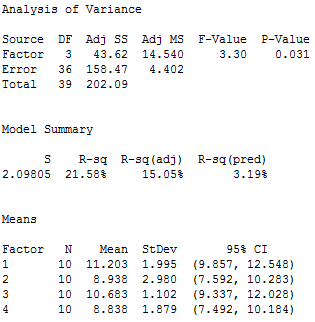
Understanding Analysis Of Variance Anova And The F Test

How To Interpret Result Of Two Way Anova Test In R Stack Overflow

Performing Anova Test In R Results And Interpretation R Bloggers

Help Online Origin Help One Two And Three Way Anova
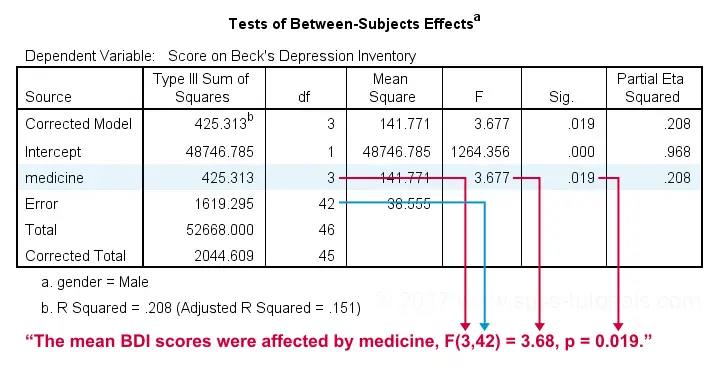
Spss Two Way Anova Tutorial Significant Interaction Effect

Basic Concepts For Anova Real Statistics Using Excelreal Statistics Using Excel
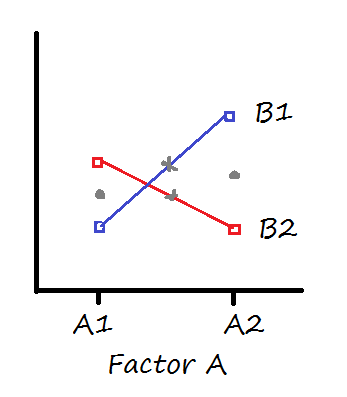
Interpreting Interactions When Main Effects Are Not Significant The Analysis Factor

One Way Anova Spss Tutorials Libguides At Kent State University
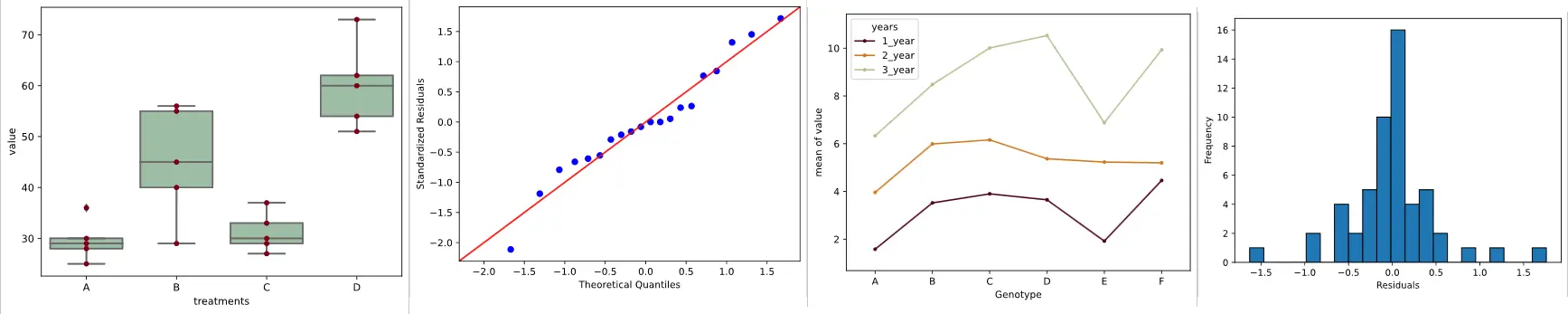
Anova Using Python Renesh Bedre
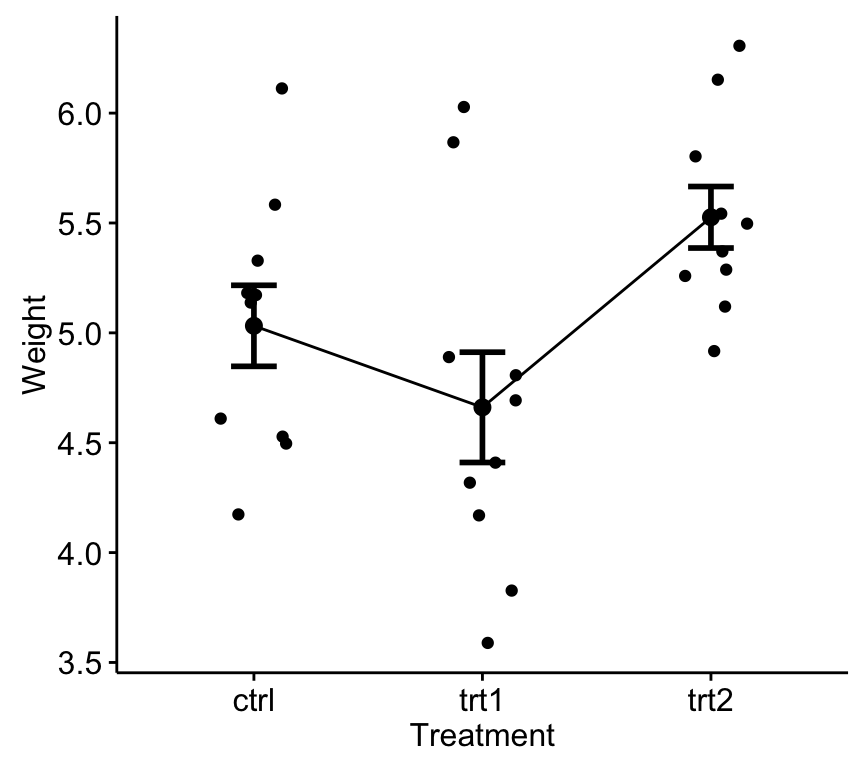
One Way Anova Test In R Easy Guides Wiki Sthda

Anova Part B Interpretation And When To Use Youtube

Anova Biology For Life

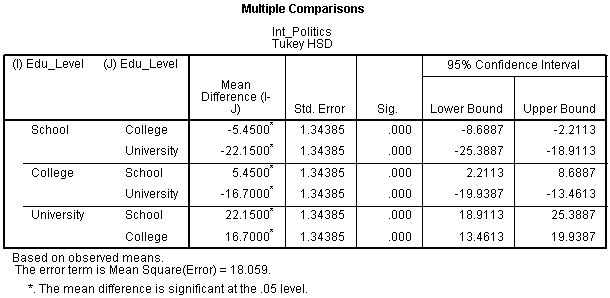
Using Post Hoc Tests With Anova Statistics By Jim
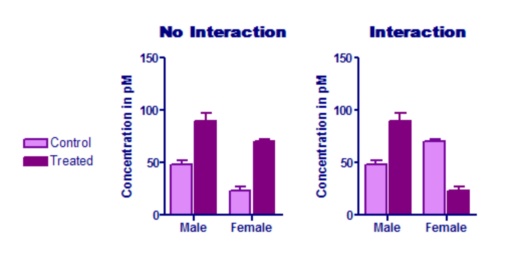
Graphpad Prism 9 Statistics Guide Interpreting Results Two Way Anova
One Way Anova Test In R Easy Guides Wiki Sthda

Interpreting The One Way Anova Oak

Spss One Way Anova With Post Hoc Tests Simple Tutorial

How To Perform A One Way Anova Test In Spss

Help Online Tutorials Two Way Anova

Interpreting Anova Table Correctly Mathematics Stack Exchange
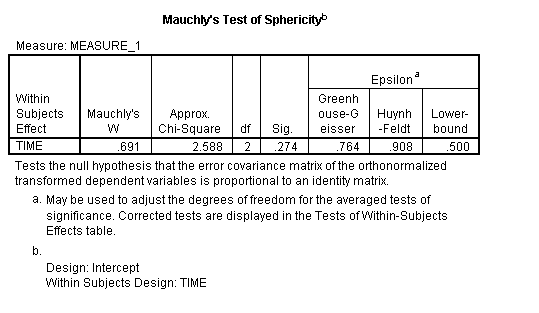
Anova Test Definition Types Examples Statistics How To
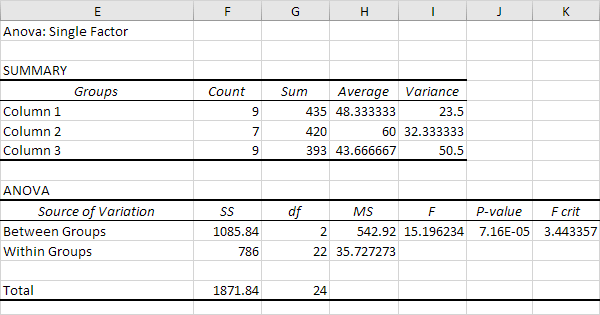
Anova In Excel Easy Excel Tutorial

How To Write The Results For An Anova Youtube
Analysis Of Variance Anova

Chapter 5 One Way Analysis Of Variance Natural Resources Biometrics
One Way Anova In Spss Statistics Understanding And Reporting The Output

Multi Factor Anova Interpretation Download Table
Spss One Way Anova Beginners Tutorial

Excel Statistics Tutorials Anova
Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial
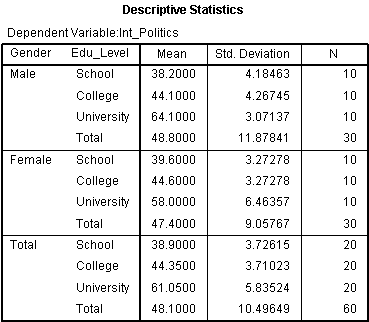
Two Way Anova Output And Interpretation In Spss Statistics Including Simple Main Effects Laerd Statistics
Anova Analysis Of Variance Super Simple Introduction
Write Up For A One Way Anova

Result Of Anova Interpretation Of Papaya Fruit Demand Download Scientific Diagram

How To Do Two Way Anova In Excel Statistics By Jim
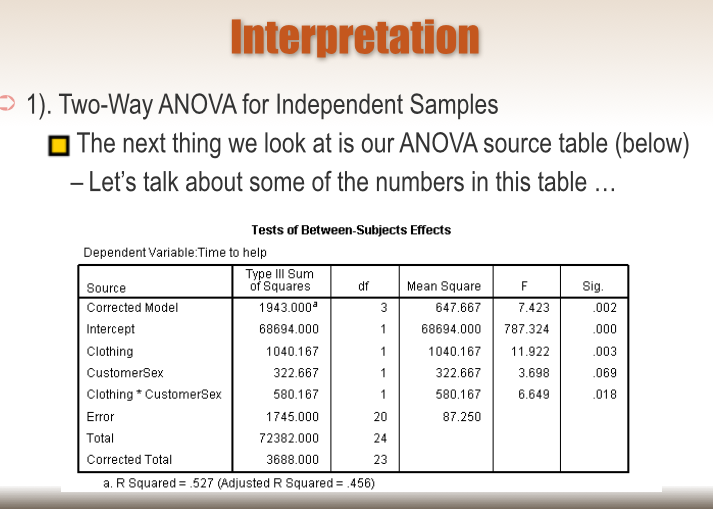
Solved Interpretation 1 Two Way Anova For Independent Chegg Com
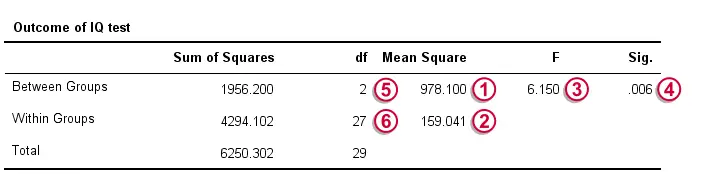
Comparison Of Population Means With Anova Table
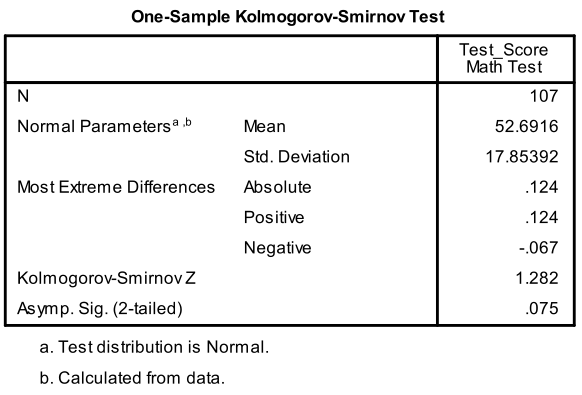
Conduct And Interpret A One Way Anova Statistics Solutions
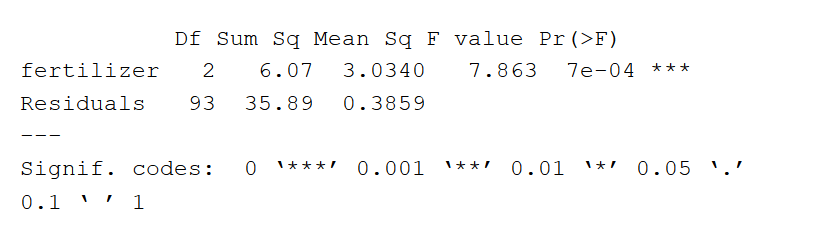
One Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples
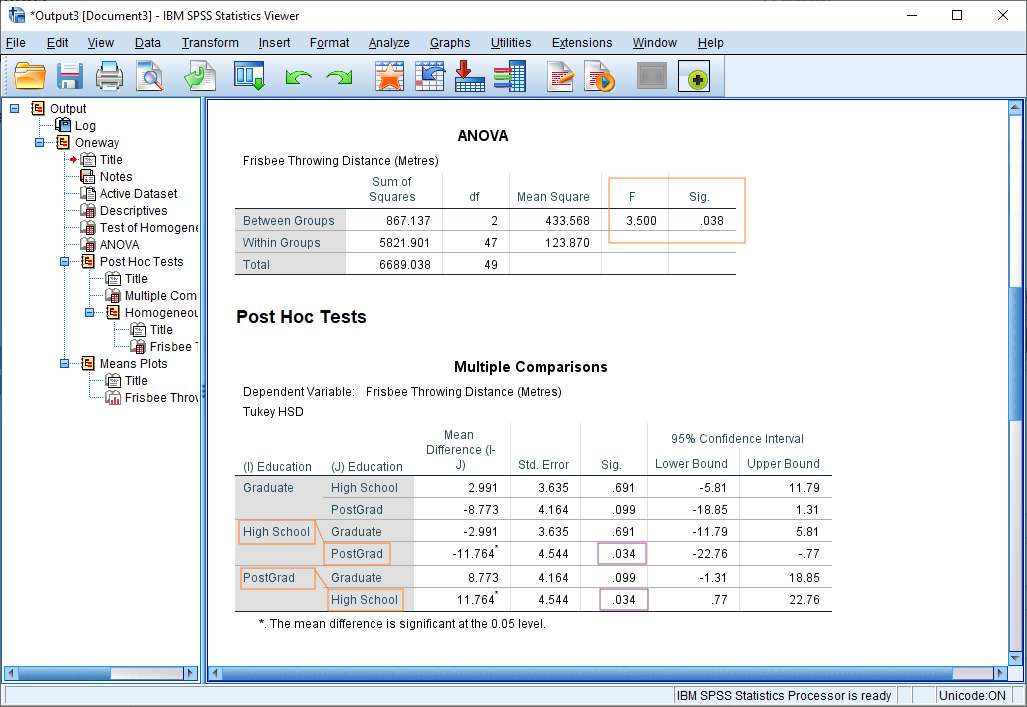
One Way Anova In Spss Including Interpretation Easy Tutorial

How Do I Interpret Data In Spss For A 1 Way Between Subjects Anova
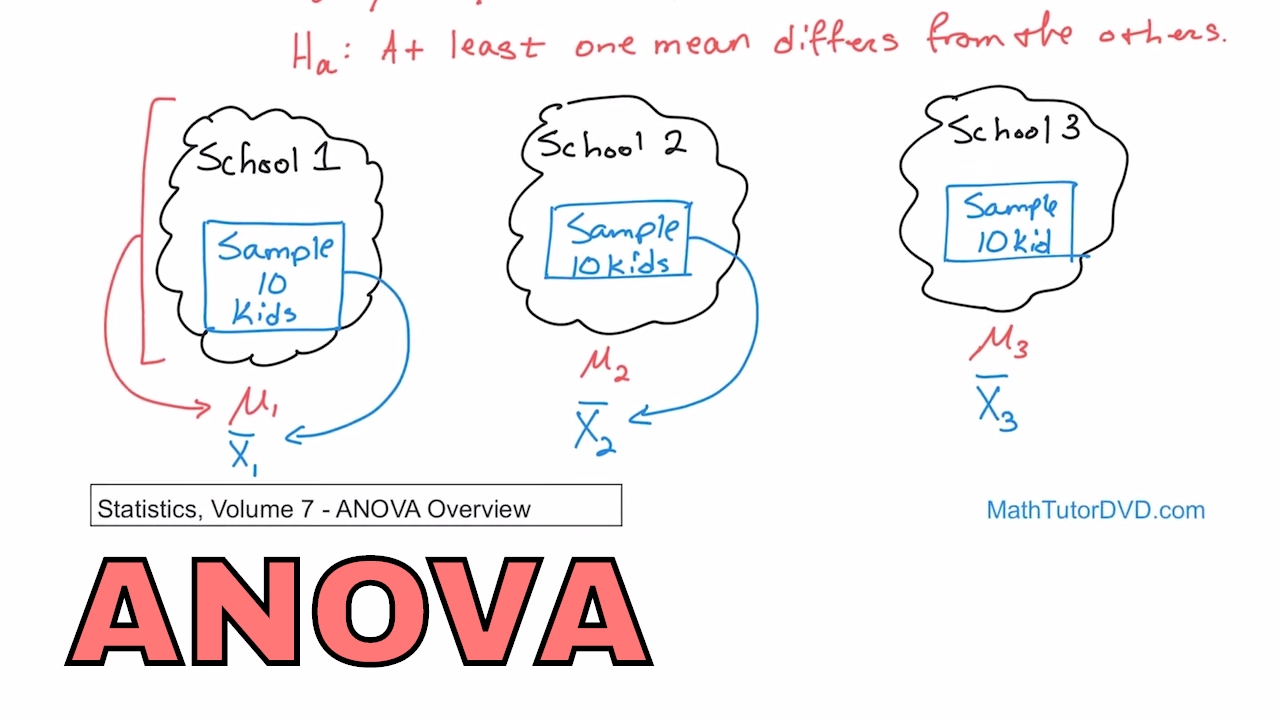
12 Analysis Of Variance Anova Overview In Statistics Learn Anova And How It Works Youtube
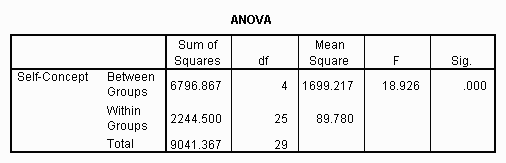
Analysis Of Variance Anova
Q Tbn And9gcriybfpvuhyiwec7edh4yuu1q60fmkxboztziajv4 Cxsralxei Usqp Cau

Perform A One Way Analysis Of Variance Anova In Excel By Dobromir Dikov Fcca Magnimetrics Medium
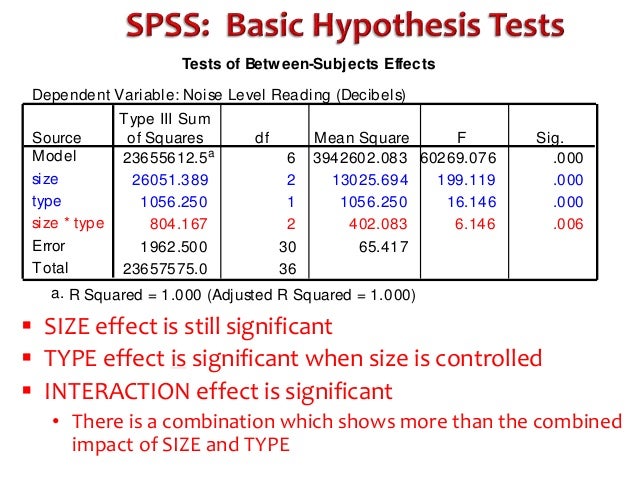
Two Way Anova Overview Spss Interpretation

How To Describe The Results Analyzed By Two Way Anova



