Mobile Phase
The mobile phase is a suitable liquid solvent or mixture of solvents Producing a paper chromatogram You probably used paper chromatography as one of the first things you ever did in chemistry to separate out mixtures of coloured dyes for example, the dyes which make up a particular ink.
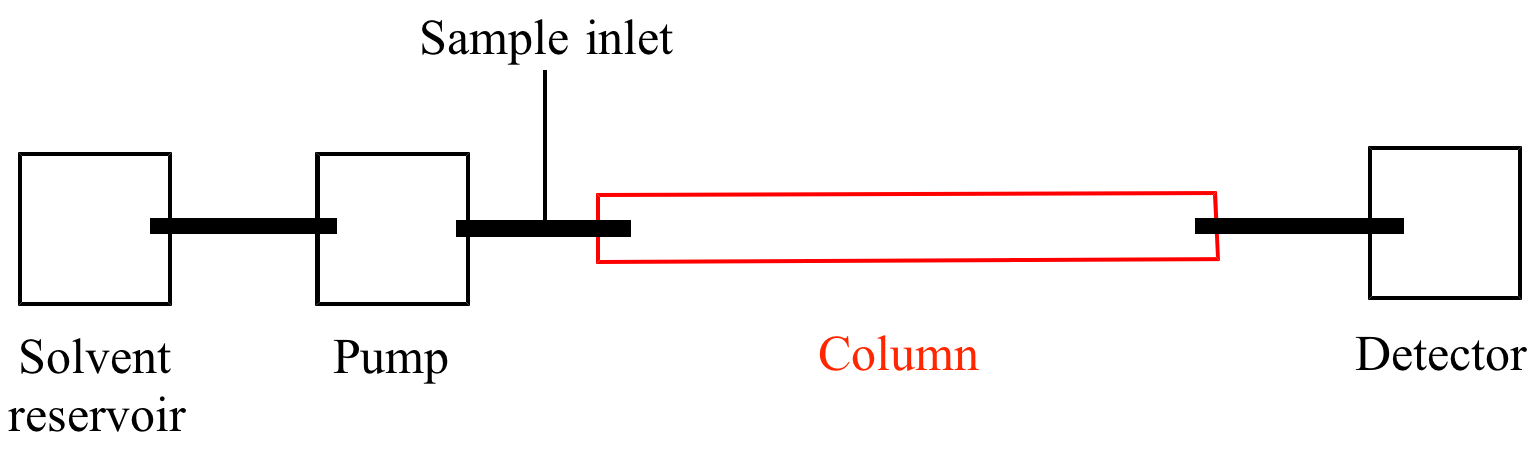
Mobile phase. The solvents used for the mobile phase are mixed before the pump Therefore, the mixed mobile phase is in a supersaturated condition before it gets to the pump Outgassing is promoted if the system undergoes any slight drop in pressure or if sites of nucleation are encountered. Noun Chemistry (In chromatography) the liquid or gas which carries the sample by diffusion through the stationary, adsorbing medium. The mobile phase carries the sample through a packed or capillary column that separates the sample’s components based on their ability to partition between the mobile phase and the stationary phase.
Just to refresh our memories, normal phase thin layer chromatography is performed on a piece of glass plate that is coated with a thin layer of silica Here, silica acts as the stationary phase and the solvent in which the plate is dipped and that runs up the plate by capillary action is the mobile phase. Mobile phases compatible for LCMS As MS operates in high vacuum, it is necessary to ensure that the LC parameters and mobile phases (liquid inlet) are compatible to MS Usually when switching from LC to LCMS analysis, the current LC conditions can be used if the mobile phase is volatile. Classification by the Composition of the Mobile Phase To tune the retention of the vast number of known compounds, the mobile phase in LC is usually a mixture of two or more solvents Isocratic technique In this technique, the mobile phase has a constant composition, for example acetonitrile–water 7228.
The Active Mobile Phase Conditioner The Caloratherm was designed to eliminate band broadening and enhance detector ionization when performing high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) separations As the liquid mobile phase enters the column located inside of the column oven, the mobile phase temperature must match the column temperature. 5 Mobile phase Ideal requirements of mobile phaseIt should be safe It should be non toxic It should be easily available It is not destory sample Chemically inert As per ICH guide lines mainly three types of the solvent ClassI Class II Class – III. Typically, the mobile phase consists of a base solvent (normal phase) or water (reverse phase) and one or more salts, acids, and buffers Certain characteristics of the mobile phase, including pH, concentrations, purity, etc, can alter the effectiveness of the mobile phase and increase or decrease the resolution.
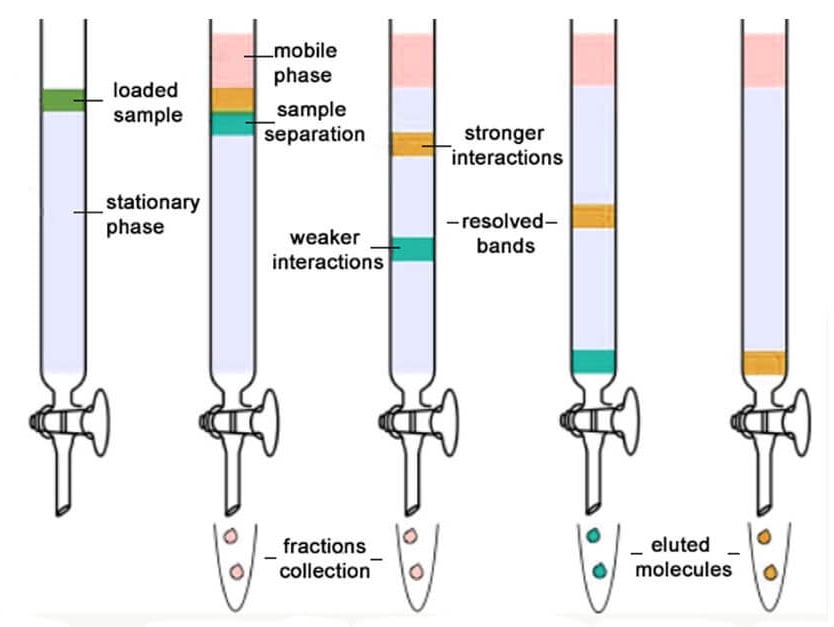
The mobile phase flows through the packed bed or column The sample to be separated is injected at the beginning of the column and is transported through the system by the mobile phase In their travel through the column, the different substances distribute themselves according to their relative affinity for the two phases. The heating unit for the mobile phase heaters consists of two lengths of tubing cast into a solid metal block One coil can be used to heat lower flow rates while two coils can be connected in series for increased heating capacity. Tetrahydrofuran (THF), widely used as a mobile phase for GPC, attacks the CTFE valve stems and TFE/propylene orings used in the standard Five Valve Cap This special THFresistant version has 316 stainless steel wherever the standard system has CTFE, and Kalrez® orings in place of the.
• For chromatography to work effectively, the components of the mobile phase need to separate out as much as possible as they move past the stationary phase That's why the stationary phase is often something with a large surface area, such as a sheet of filter paper, a solid made of finely divided particles, a liquid deposited on the surface. In a reverse phase with aqueous mobile phase the analyte will spend less time in hydrophobic interactions with stationary phase and more time forming hydrogen bonds with the aqueous part of the mobile phase as compared to the neutral molecule, result will be less retention of polar molecules. In a reverse phase with aqueous mobile phase the analyte will spend less time in hydrophobic interactions with stationary phase and more time forming hydrogen bonds with the aqueous part of the mobile phase as compared to the neutral molecule, result will be less retention of polar molecules.
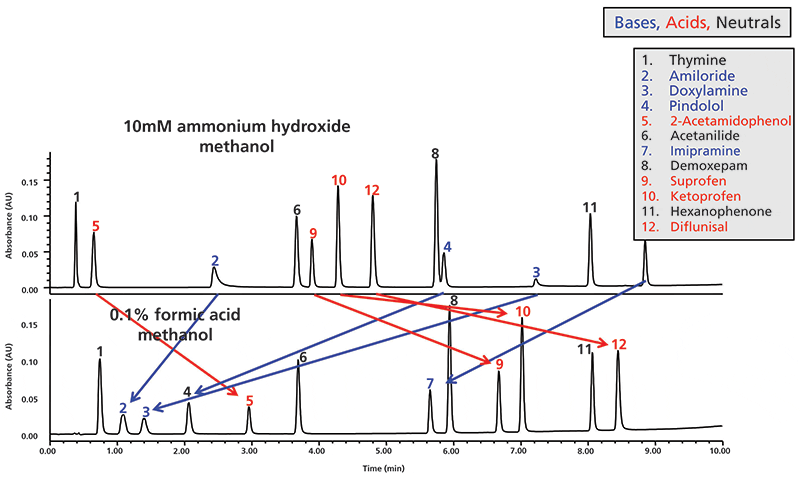
A mobile phase at acidic pH of 25–3 is a good starting point for most pharmaceutical applications because the low pH suppresses the ionization of most acidic analytes resulting in their higher retention 2,3 Common acids used for mobilephase preparations are phosphoric acid, formic acid, and acetic acid Low pH also minimizes the interaction of basic analytes with surface silanols on the silica packing (because silanols do not ionize at acidic pH). With silica and alumina the more the mobile phase is polar the more the solutes are eluted towards the front of the solvent, towards large values of Rf (Rf ≥ 06) Conversely, the more the mobile phase is nonepolar, the less the solutes are entrained and the closer they stay to the deposit line with low values of Rf (Rf ≤ 01). In LC separations, the mobile phase pH determines the ionisation state of ionisable analytes The mobile phase pH can therefore be varied and used as a powerful tool to control analyte retention, peak shape and selectivity This short article explains how retention of acidic, basic and neutral analytes is affected by mobile phase pH, as well as the requirements for carrying out separations at high and low pH.
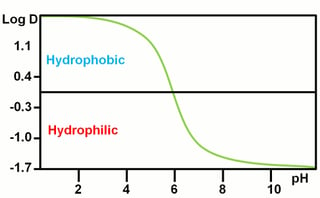
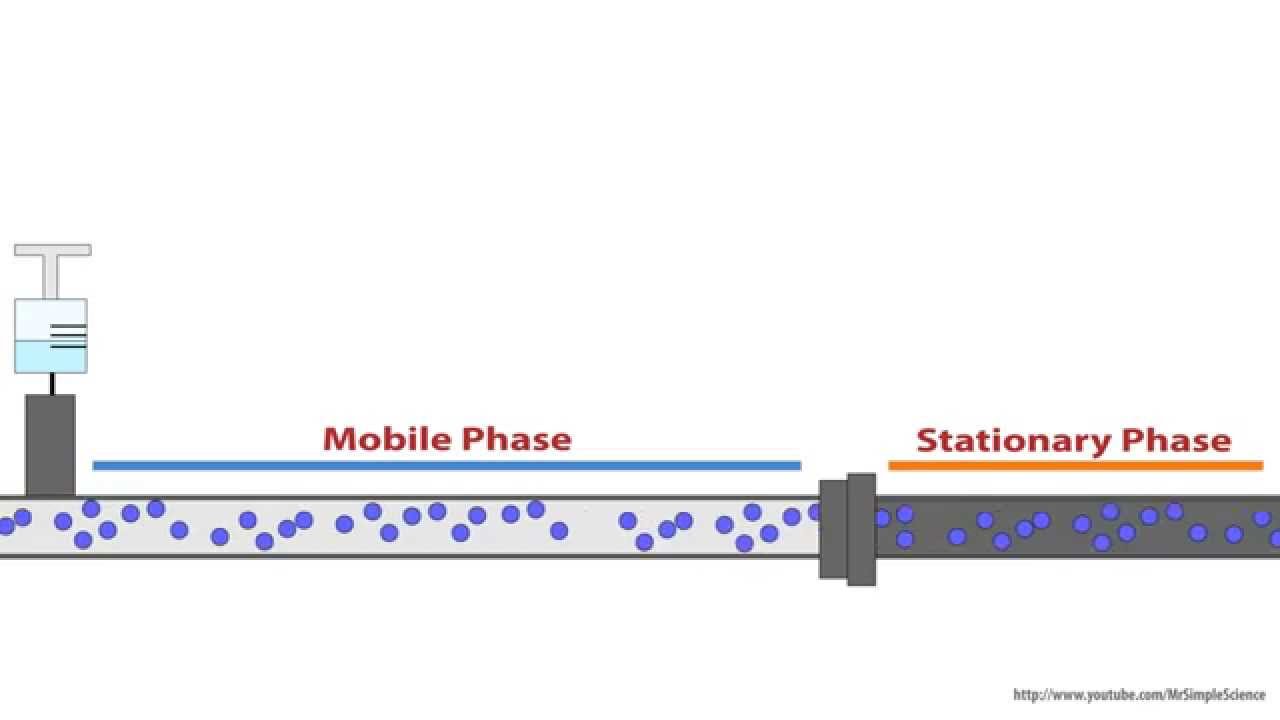
The pH of the mobile phase should be selected in order to enhance the hydrophilicity of the analytes All the analytical scientists that work with reversedphased liquid chromatography (RPLC) know really well that the pH of the mobile phase determines the ionization state of the analytes That remains valid also in HILIC, but differently from RPLC, the pH of the HILIC mobile phase should be selected with the intention of bringing the analytes in their ionic form. The substance that moves the sample through the machine In HPLC the mobile phase is a liquid made up of an organic solvent, ultrapure water and other ingredients to ensure its compatibility with the sample GC uses gas for its mobile phase Gases used include helium, nitrogen, argon or hydrogen, depending on what is being analyzed Secondly, as samples travel over chromatography columns, the. Chromatography is a method by which a mixture is separated by distributing its components between two phases The stationary phase remains fixed in place while the mobile phase carries the components of the mixture through the medium being used.
In gas chromatography mass spectrometry urine drug screening, the mobile phase is one of two phases, the other being the stationary phase, that the sample solution enters into during testing The mobile phase is an inert gas that the sample is injected into that will carry it through the stationary phase, which is normally a solid. The mobile phase carries the sample through a packed or capillary column that separates the sample’s components based on their ability to partition between the mobile phase and the stationary phase. MOBILE PHASE BAGS ARE QUALITY TESTED FOR Tensile Strengthis the maximum amount of stress that a material can handle before breaking Elongationis the amount of extensions of an object under stress, usually expressed as a percentage of original length.
Sometimes when working with acidic or basic analytes buffers are not always used, a small percentage of acids or bases like TFA, Formic Acid and Ammonium Hydroxide are sufficient to neutralize the ionic species in the samples These mobile phase additives are called pH modifiers and they can only effectively work at their specific pKa/pKb values. The mobile phase This is the chromatography liquid and it helps the sample move over the stationary phase The mobile phase used is a liquid or gas and it should be free of particle matter and other impurities Technically, the mobile phase should have opposite polarity to that of stationary phase material. Principally the process has two physical phases, solid and liquid The solvent carrying the mixture is the mobile phase since it moves along the stationary phase or the absorbent column We will be discussing the solvents used in the HPLC mobile phase as their selection determine how the analytes can be separated.
The mobile phase is a suitable liquid solvent or mixture of solvents Producing a paper chromatogram You probably used paper chromatography as one of the first things you ever did in chemistry to separate out mixtures of coloured dyes for example, the dyes which make up a particular ink. In gas chromatography, the components of a sample are dissolved in a solvent and vaporized in order to separate the analytes by distributing the sample between two phases a stationary phase and a mobile phase The mobile phase is a chemically inert gas that serves to carry the molecules of the analyte through the heated column. Because mobile phase composition can be easily changed, and also because it is common in HPLC to use mobile phase gradients, changes in the mobile phase are commonly used for modifying and improving a separation The basic composition of the mobile phase is, as expected, related to the type of HPLC and of the column used for the separation.
Wiktionary (300 / 7 votes)Rate this definition mobile phase (Noun) The liquid or gas that flows through a chromatography system, moving the materials to be separated at different rates over the stationary phase. Tetrahydrofuran (THF), widely used as a mobile phase for GPC, attacks the CTFE valve stems and TFE/propylene orings used in the standard Five Valve Cap This special THFresistant version has 316 stainless steel wherever the standard system has CTFE, and Kalrez® orings in place of the. The heating unit for the mobile phase heaters consists of two lengths of tubing cast into a solid metal block One coil can be used to heat lower flow rates while two coils can be connected in series for increased heating capacity.
The mobile phase flows through the packed bed or column The sample to be separated is injected at the beginning of the column and is transported through the system by the mobile phase In their travel through the column, the different substances distribute themselves according to. Mobile phase filtration is performed prior to placing the solvent into the solvent reservoir Buffered mobile phase solvents require daily filtration with a 02 μm filter to eliminate microbial growth that could increase the baseline The primary concern when choosing a solvent filter is solvent compatibility with the filter material. Supelco Mobile Phase Degassing System 4 Channel 05 ml/min Flow Range Validation output satisfies system compliance Smart sensor detects leaks and communicates with vacuum pump LED indicates degassing status Unprecedented 4 year warranty The Supelco Mobile Phase Degassing system with its smart sensor not only detects and alerts you to leaks, it also communicates with the vacuum pump.
As the mobile phase strength increases, the analyte will begin to partition into the mobile phase and move along the column At some point, the analyte may be wholly partitioned into the mobile phase and will be moving with the same velocity as the mobile phase. The mobile phase used in HPLC are two types and they are the isocratic type and the other is the gradient type In isocratic type, the mobile phase has a single solvent or more than one solvent yet the ratio of the composition is fixed throughout the HPLC analysis In gradient type, the number of solvents in the mobile phase is two or more. Consequently, at the beginning of the run when the mobile phase strength is low, the analyte will be concentrated into the stationary phase at the head of the column As the mobile phase strength increases, the analyte will begin to partition into the mobile phase and move along the column.
Each mobile phase heater is custom made to accommodate the customer’s flow rate and temperature requirements without excess holdup volume The TL600 accommodates mobile phases flowing as fast as 100mL/min and temperatures as high as 90°C For higher flow rates, Timberline offers a TL2500 Mobile Phase Heater. The mobile phase in reversedphase chromatography is a mixture of water or buffer with a polar organic solvent such as methanol, acetonitrile, isopropanol (IPA), or tetrahydrofuran (THF) The elution strength increases roughly in this order The alcohols are proton donors while acetonitrile is a proton acceptor. Principally the process has two physical phases, solid and liquid The solvent carrying the mixture is the mobile phase since it moves along the stationary phase or the absorbent column We will be discussing the solvents used in the HPLC mobile phase as their selection determine how the analytes can be separated.
MOBILE PHASE BAGS ARE QUALITY TESTED FOR Tensile Strengthis the maximum amount of stress that a material can handle before breaking Elongationis the amount of extensions of an object under stress, usually expressed as a percentage of original length Yield Strengthis the minimum amount of stress on a material at which it begins to permanently deform. Convenient kits for easy mobile phase management Protect your mobile phase from evaporation and contamination, and your lab from harmful vapors Includes one 3port MobiCap GL45 bottle top ( cat# 276 ) Includes PTFE tubing 1/8" OD x 0063 mm ID x 3 m ( cat# ) Includes two 1/16" connection sparger filters one 2 μm ( cat# 277) and one 10 μm ( cat# 278 ).
Hilic Mobile Phase Ph

Components Of Column Chromatography A Mobile Phase And Delivery System Download Scientific Diagram

Basics Of Chromatography Stationary And Mobile Phase In Hindi Urdu Youtube
Mobile Phase のギャラリー
Separations Free Full Text The Development Of Silica Hydride Stationary Phases For High Performance Liquid Chromatography From Conception To Commercialization Html

Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Chromatography Mobile Phase Stationary Phase
3
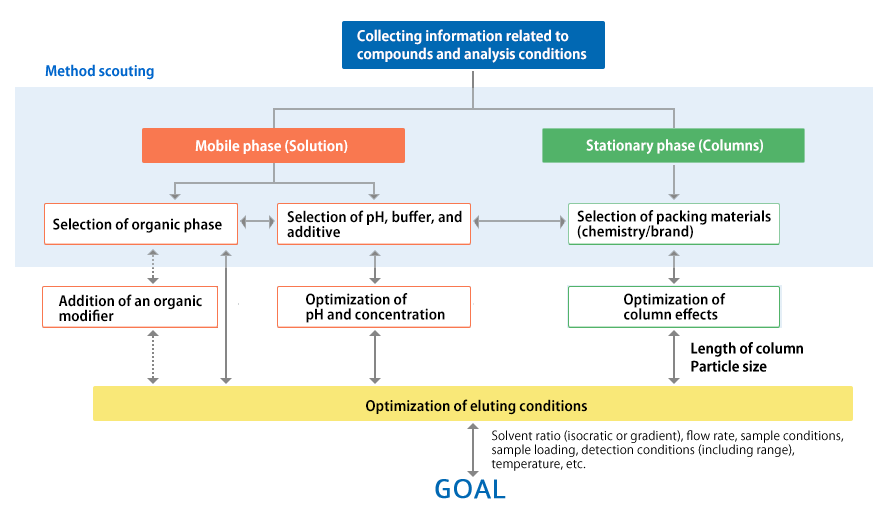
Guides For Method Development Ymc Co Ltd

New Page 1

How Column Chromatography Works To Separate Proteins Goldbio

How To Optimize Your Mobile Phase To Improve Selectivity And Resolution In Chromatography

Solved What Is The Main Purpose Of The Mobile Phase In Ch Chegg Com

The Basics Of Running A Chromatography Column
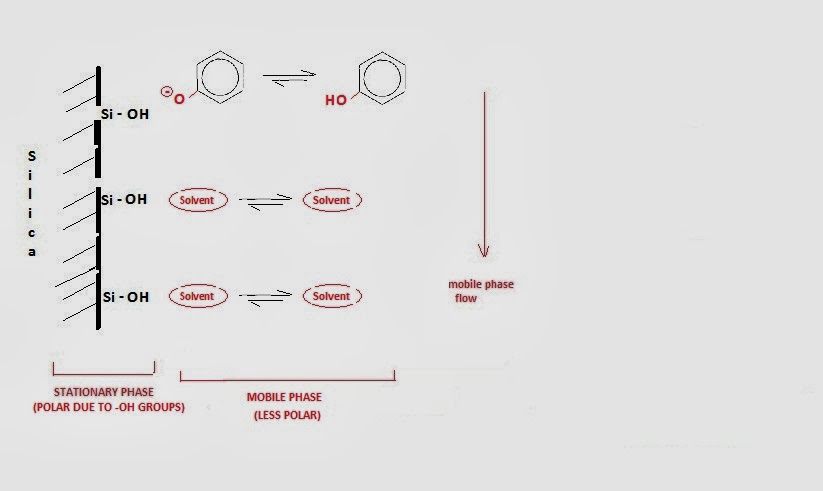
Chemistry Net Normal Phase Liquid Chromatography Lc Hplc

Principles Of Chromatography Stationary Phase Article Khan Academy

M

Normal Phase Liquid Chromatography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
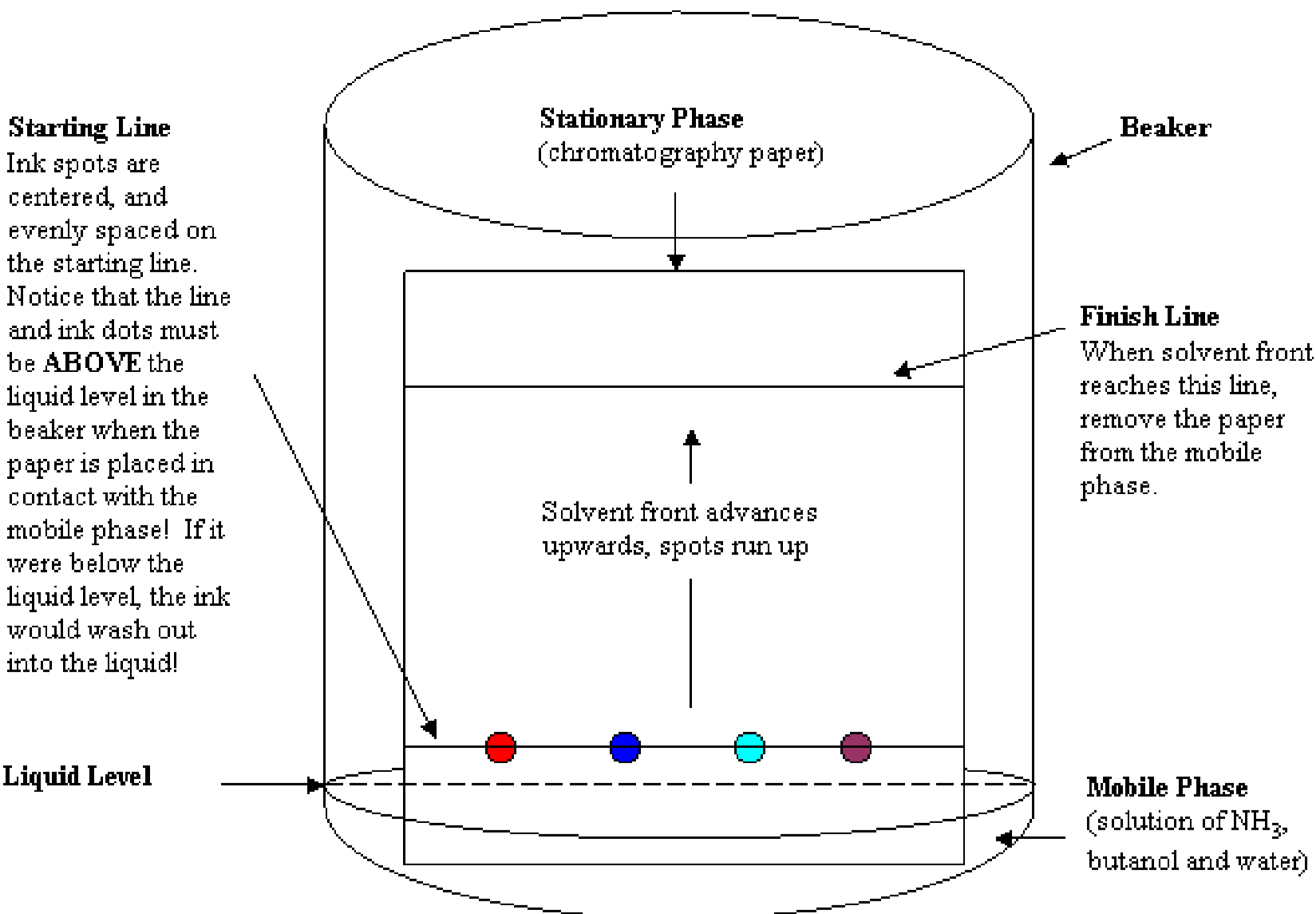
2 Paper Chromatography Of Gel Ink Pens Experiment Chemistry Libretexts

Running Hplc With Hydrophobic Stationary Phase And Aqueous Mobile Phase Chromatography Today
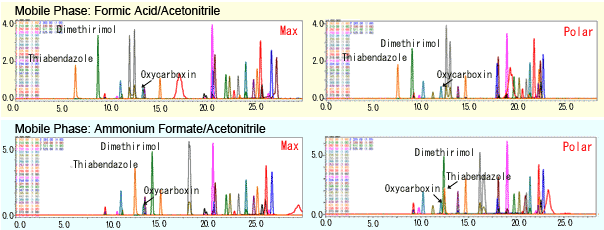
Separation Conditions4 Examining Mobile Phase Ratios And Improving Separation Shimadzu Shimadzu Corporation
3

Falling Victim To One Of Lc S Classic Blunders Mismatching Your Diluent And Mobile Phase Chromablography Restek S Chromatography Blog
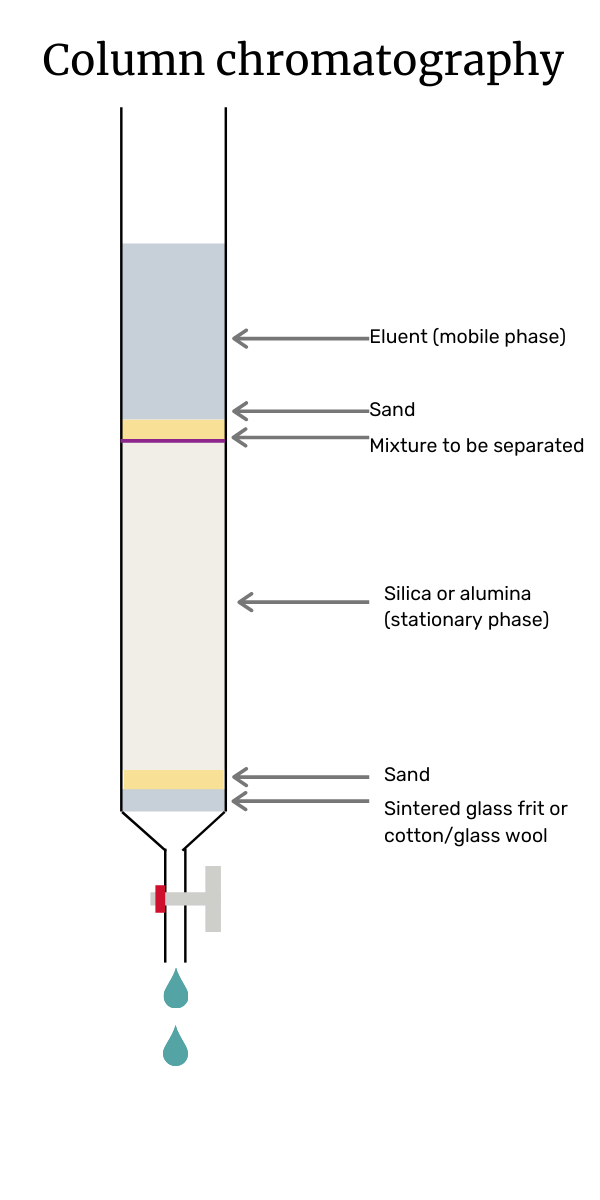
What Is Chromatography And How Does It Work Bioanalysis Zone

The Principle And Method Of Chromatography Mbl

Tlc Introduction
Modern Trends And Best Practices In Mobile Phase Selection In Reversed Phase Chromatography Chromatography Online
Guides For Method Development Ymc Co Ltd

Considerations For Mixing Of Hplc Mobile Phase Solvents
14 Types Of Chromatography Definition Principle Steps Uses
Hplc The Stationary Phase Animated Youtube

Principles Of Chromatography Stationary Phase Article Khan Academy
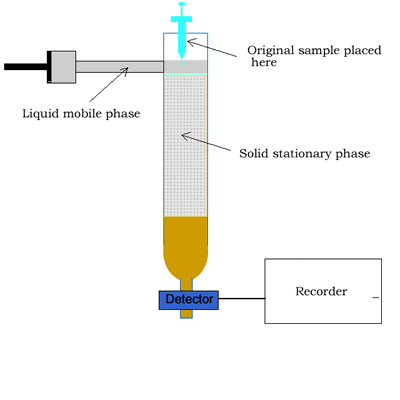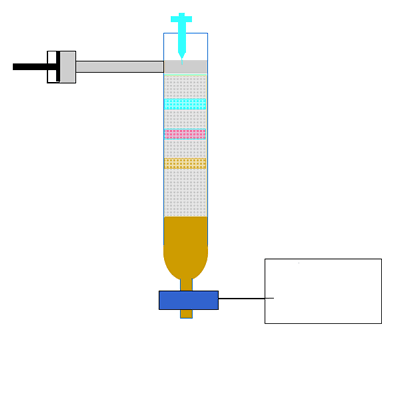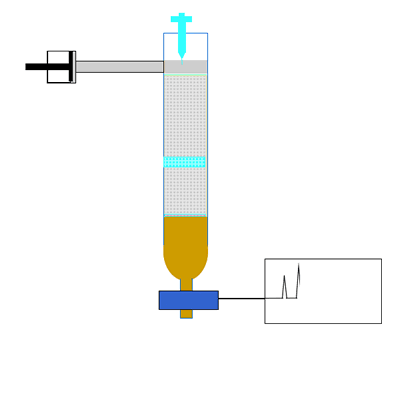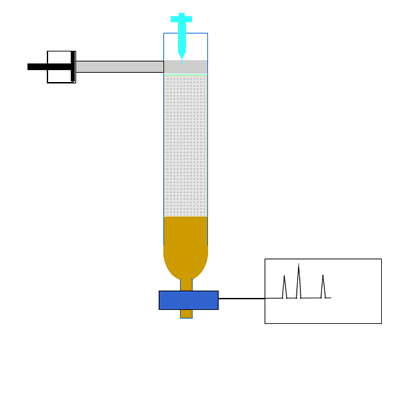
Chemistry Analytical Chromatography

China Customized Mobile Phase Hplc Cap Manufacturers Discount Mobile Phase Hplc Cap Auwii
/chapter4/pages3and4/page3and4_files/tlcsetup.png)
Chapter 4

Mobile Phase Bottle Capacity Standardised Universal Instruments Id

Chromatography Revise Im

We Need To Talk About Flow Rate And Column Efficiency In Chromatography

Gas Liquid Chromatography
Stationary Phase Mass Transport Broadening Chemistry Libretexts

Proteomics Protein Separations Chromatography Stationary And Mobile Phases Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Chromatography

Mobile Phase In Chromatography
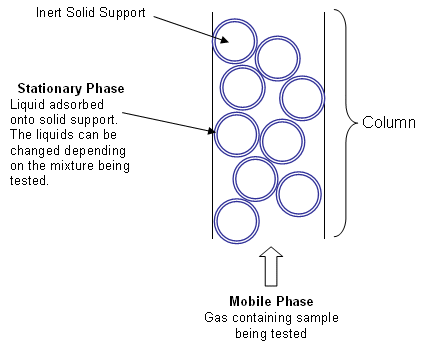
Gas Liquid Chromatography

Mobile Phase Description Label Lrmp Blu Helixtags
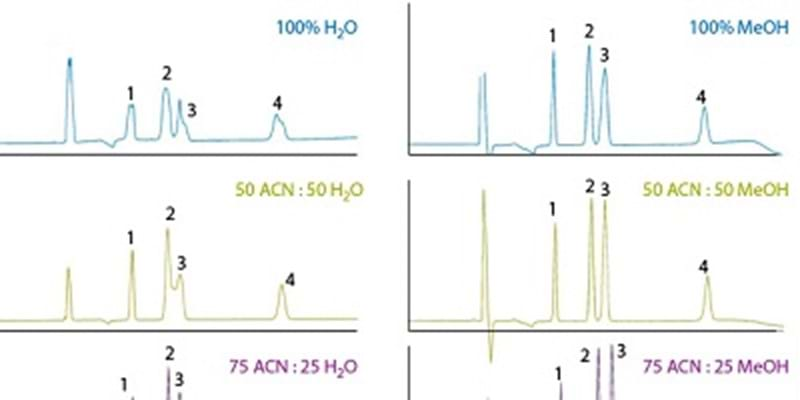
10 Tips For Hilic Mobile Phase Optimization

Introduction To Chromatography 2 Mobile Phase Youtube

Modern Trends And Best Practices In Mobile Phase Selection In Reversed Phase Chromatography Chromatography Online

Introduction To Chromatography Ppt Video Online Download

Chromatography Techniques

Chromatography Main Concepts And Calculations

Mourne Training Services Help On Expiry Dates For Hplc Mobile Phase
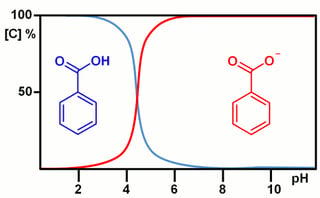
Hilic Mobile Phase Ph

Mobile Phase Preparation Steps To Take For Ideal Analysis

Selectivity And The Hplc Mobile Phase Chromablography Restek S Chromatography Blog

Hplc Normal Phase Vs Reverse Phase Video Technology Networks
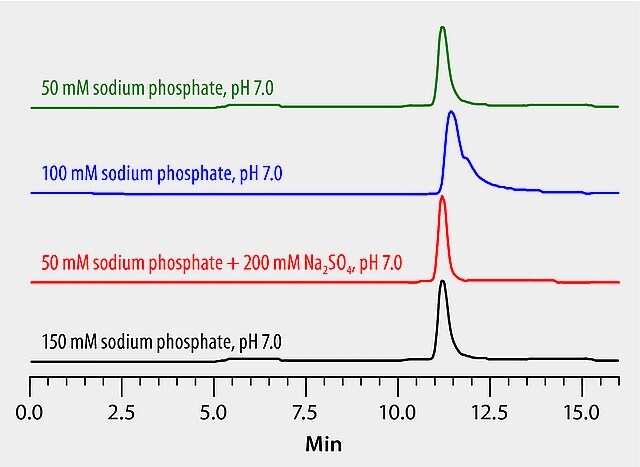
Mobile Phase Optimization In The Analysis Of Lysozyme On Zenix Sec 300 Sigma Aldrich
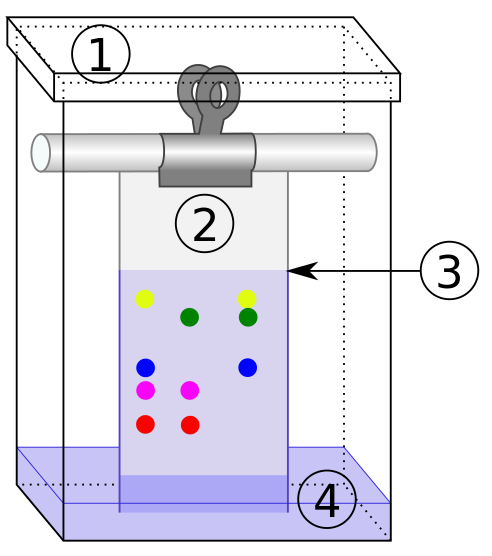
Difference Between Stationary And Mobile Phase Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
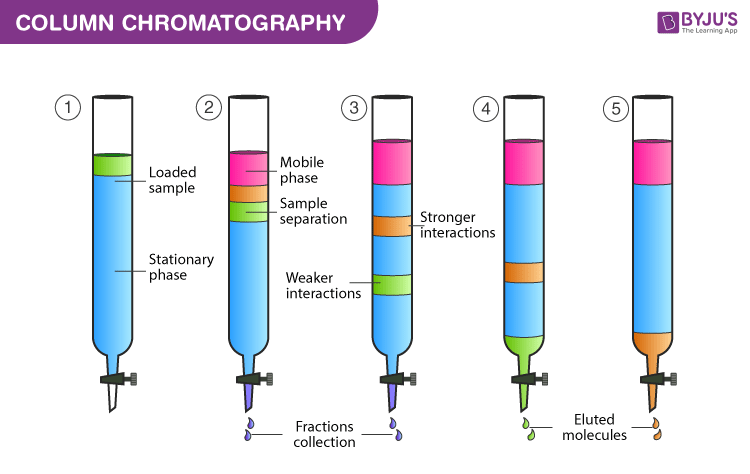
Column Chromatography Principle Procedure Applications On Byju S

Mobile Phase Preparation Steps To Take For Ideal Analysis
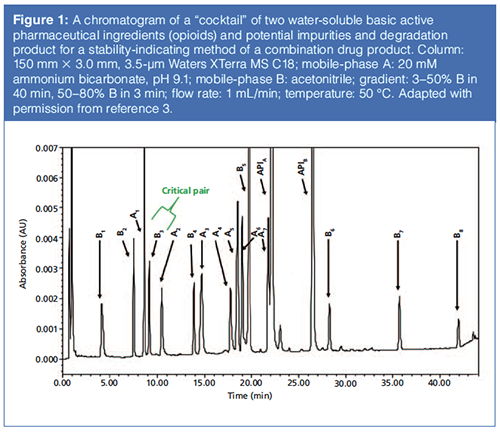
Modern Trends And Best Practices In Mobile Phase Selection In Reversed Phase Chromatography Chromatography Online

Mobile Phase 1
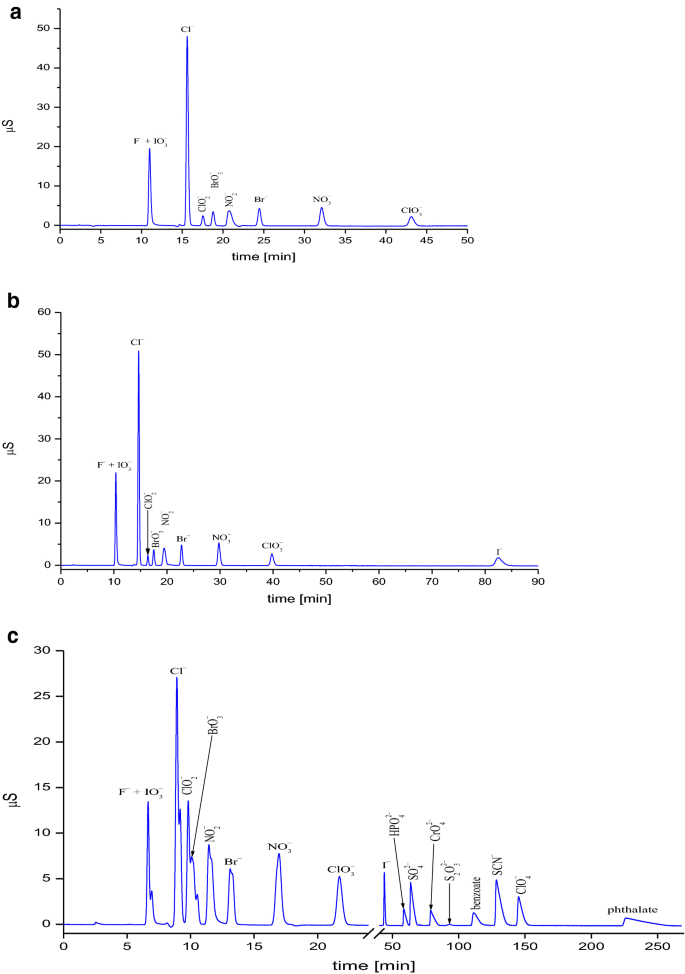
Observations On Ion Interaction Chromatographic System Reversed Phase Column H 3 Bo 3 Tbaoh Mobile Phase And The Effect Of Temperature Springerlink

Proper Mobile Phase Preparation To Minimize Contaminants Sigma Aldrich
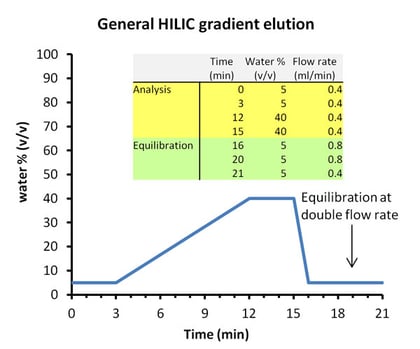
Hilic Mobile Phase Solvents

Mobile Phase And Stationary Phase Considerations

The Principle Of Iec Separation The Mobile Phase Has Ions Negatively Download Scientific Diagram

Ion Pair Chromatography In Reverse Phase Hplc

Hplc What Is The Function Of The Mobile Phase Animated Youtube

Solved In Order For A Substance To Be An Effective Mobile Chegg Com
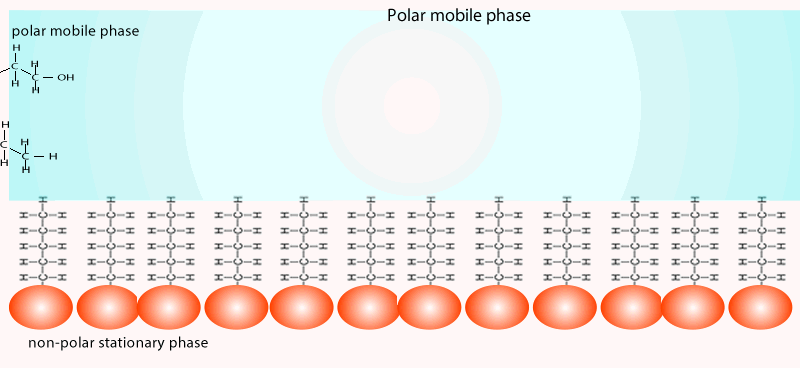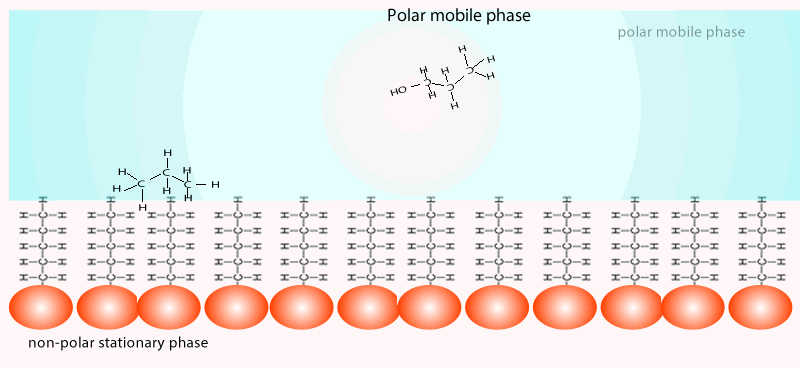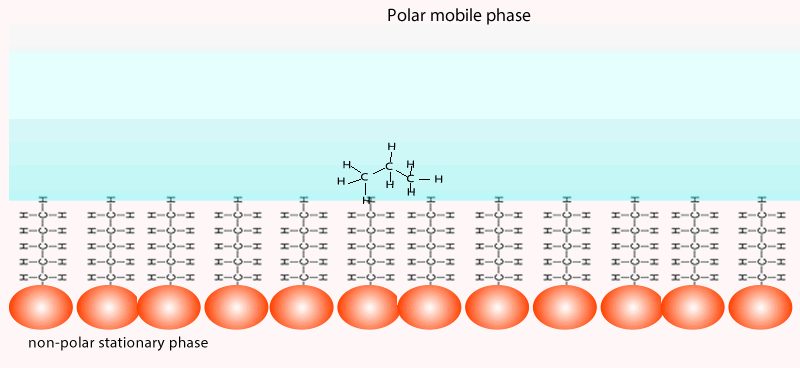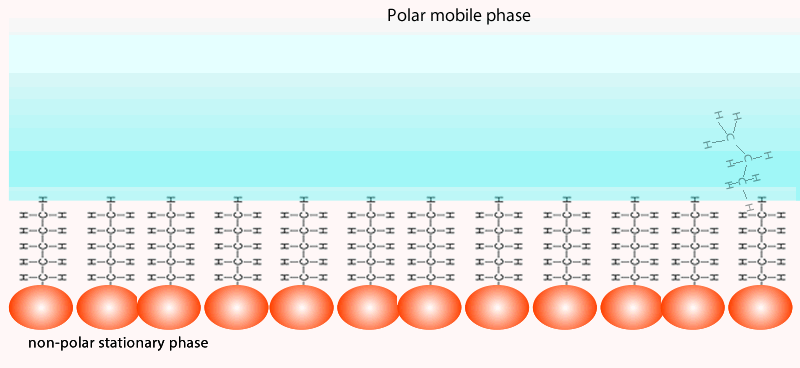
Chemistry Analytical Chromatography

Mobile Phase Composition An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
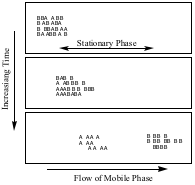
Tlc

Mobile Phase In Chromatography
Q Tbn And9gcqvnu48cj73zobsrb0w Mkk5nls4voecmjhmhtznlwyetzrpsc3 Usqp Cau
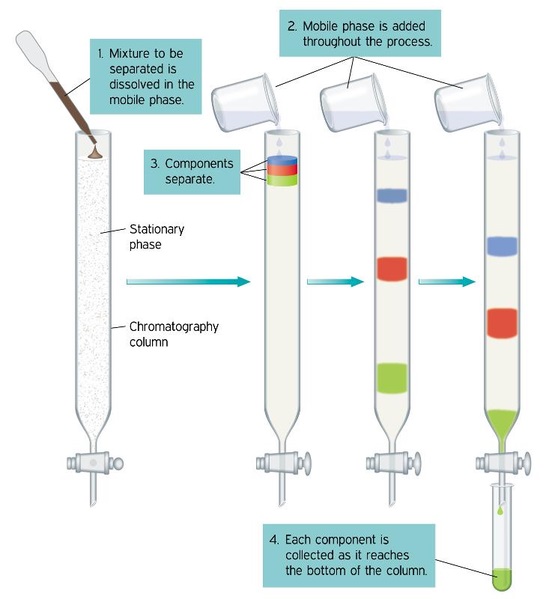
What Is The Difference Between Mobile Phase And Stationary Phase Pediaa Com

Liquid Chromatography Hplc Systems Knauer

Improve Uhplc And Lcms Analysis With A Mobile Phase Ghost Trap Filter

Effect Of Mobile Phase Composition On Retention Of 3 Compounds On Obelisc R Sielc
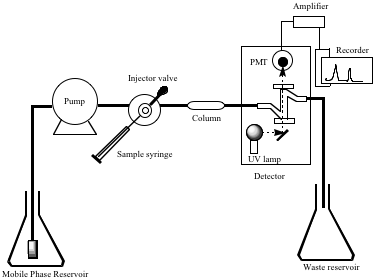
Tlc

Proteomics Protein Separations Chromatography Stationary And Mobile Phases Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

What Exactly Is Chromatography Types And Applications Rankred

Polar Compound Retention Using Aqueous Normal Phase Anp Hilic Chromatography Sigma Aldrich
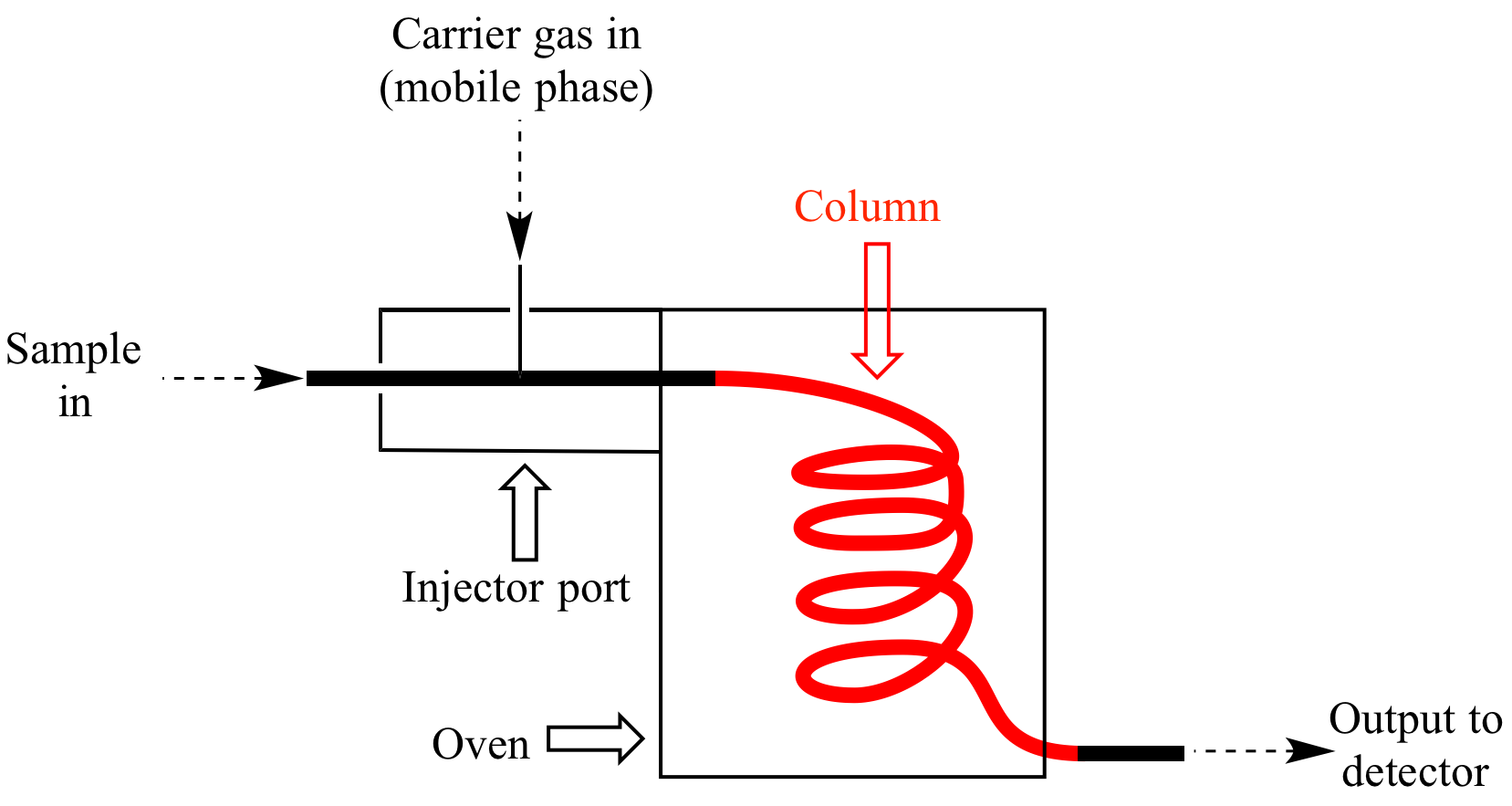
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Chromatography Mobile Phase Stationary Phase
Mobile Phase Mass Transport Broadening Chemistry Libretexts

Chromatography Wikipedia

Polarity Chart Of Stationary Phases Mobile Phases And Analytes 61 Download Scientific Diagram

Diagram Of Normal Phase Chromatography Separation The Stationary Phase Download Scientific Diagram

Gas Chromatography How A Gas Chromatography Machine Works How To Read A Chromatograph And Gcxgc Technology Networks
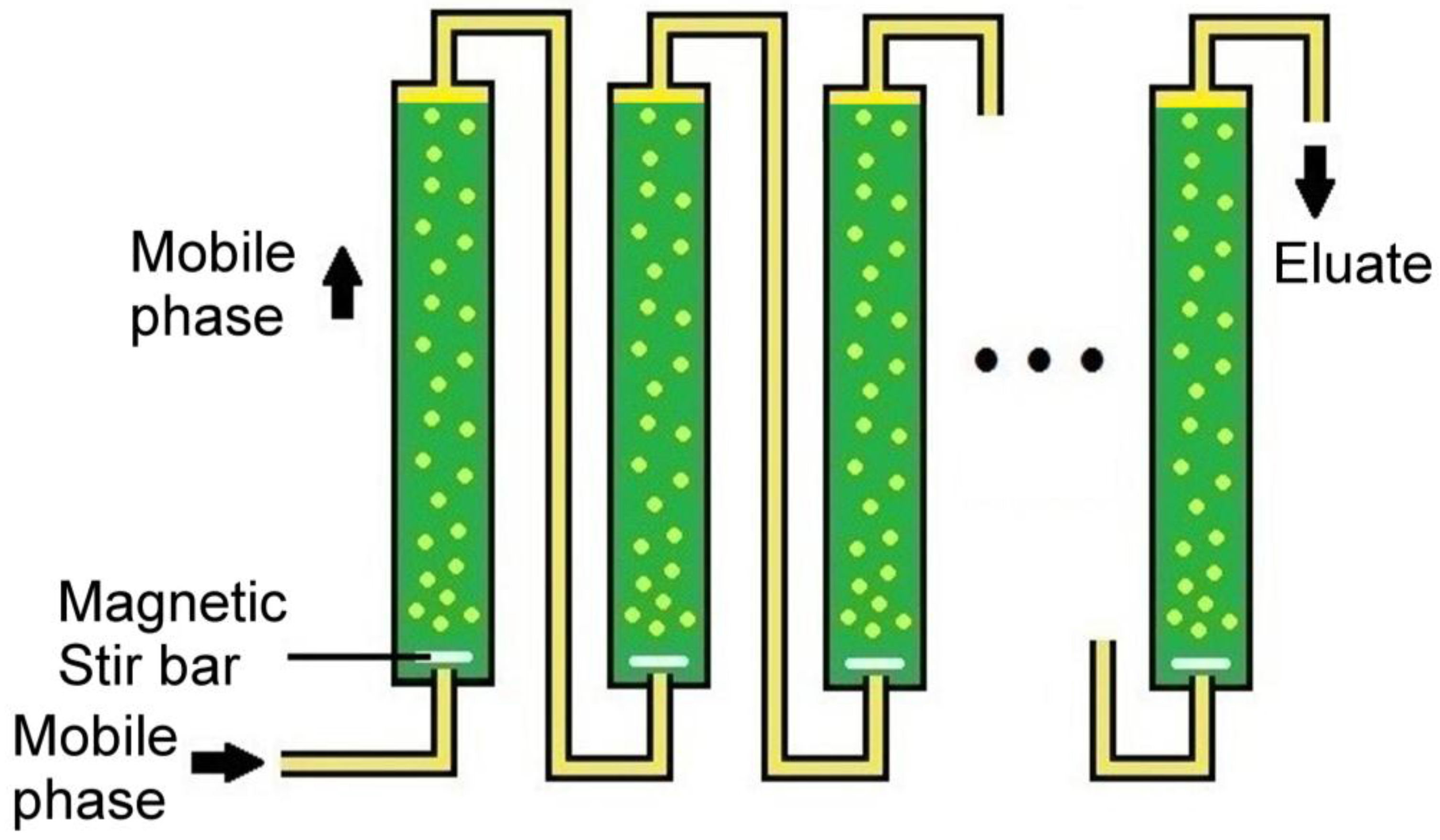
Separations Free Full Text Dispersed Mobile Phase Countercurrent Chromatography
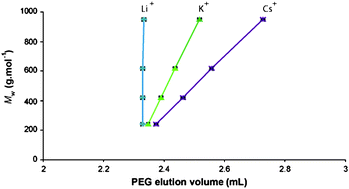
Effect Of Salt In The Mobile Phase On The Critical Conditions Of Poly Ethylene Glycol In Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Coupling Analytical Methods Rsc Publishing

Action Of Flow Rate Of Mobile Phase In Chromatography Scientific Net

Mobile Phase Reservoirs In High Performance Liquid Chromatography
Ptc Amino Acids Mobile Phase A 163 Detail Information Analytical Chemistry Laboratory Chemicals Fujifilm Wako Chemicals U S A Corporation

Mobile Phase Monitor Mpm 40 Hplc Knowledge Base

How Does High Performance Liquid Chromatography Work Waters

Beginner S Guide To Convergence Chromatography 2 Waters
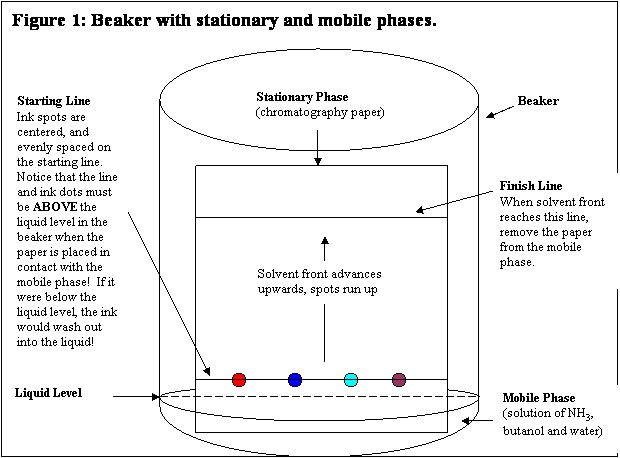
Question 7eb Example

Beginner S Guide To Convergence Chromatography 2 Waters
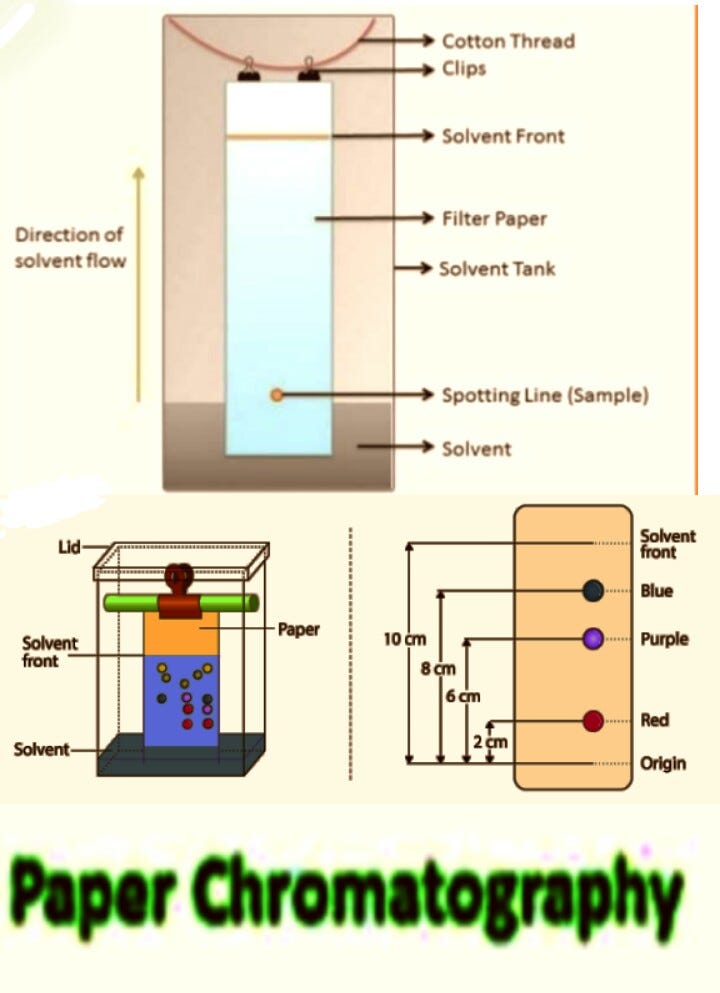
Chromatography Definition By Lab Technician Medium

Pure Water As A Mobile Phase In Liquid Chromatography Techniques Sciencedirect

Lc Technical Tip Sample Diluent Effects

Chromatography The Biotech Notes

Tlc Fundamentals Stationary Mobile Phase Choice Part 4
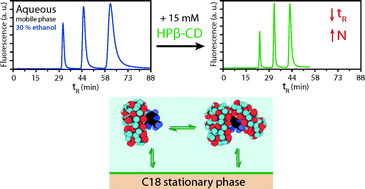
Eco Friendly Liquid Chromatographic Separations Based On The Use Of Cyclodextrins As Mobile Phase Additives Green Chemistry Rsc Publishing



