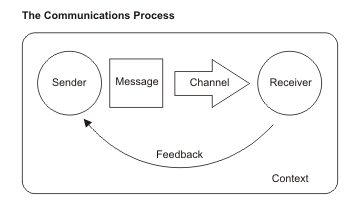
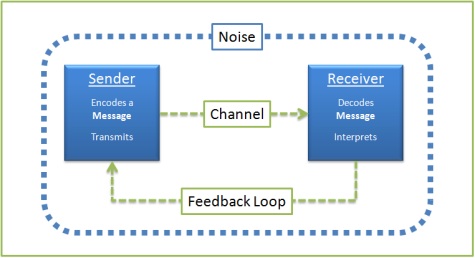
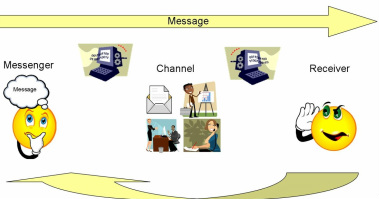
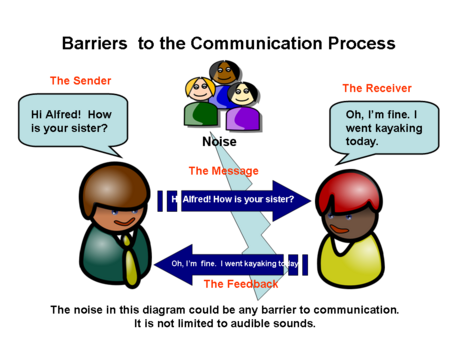
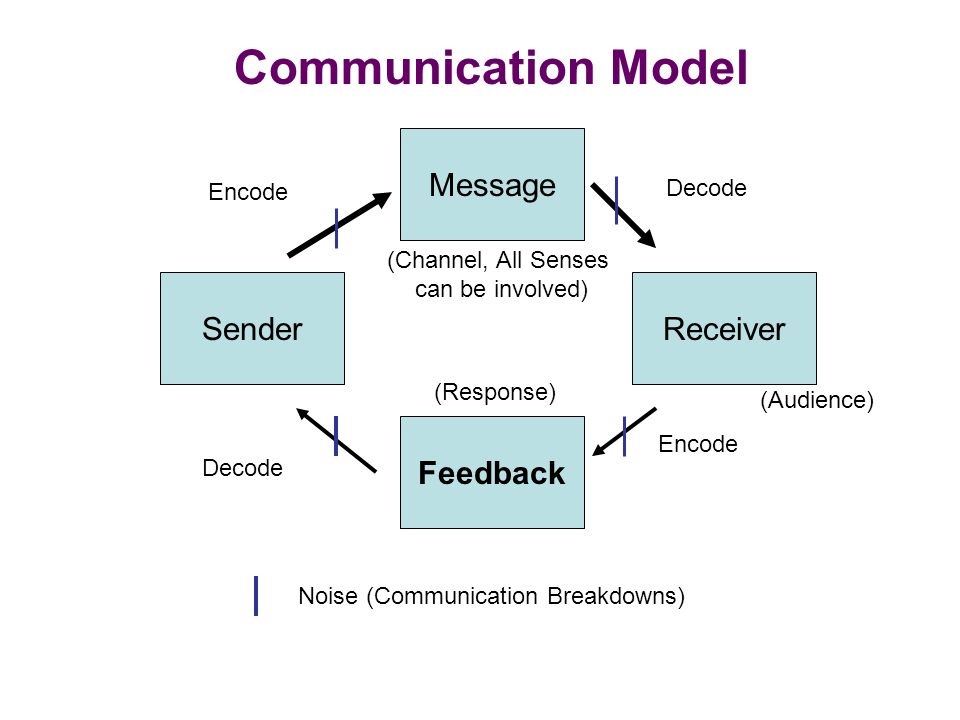
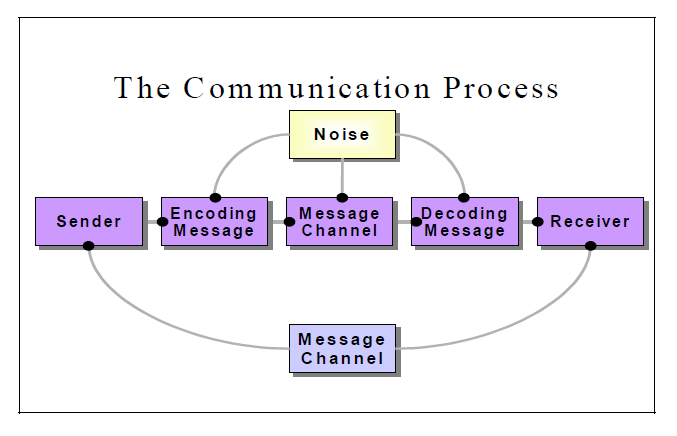
Sender Receiver Message Channel Feedback
Receiver The receiver is one who is intended to receive the message sent by sender Feedback Feedback constitutes the information which the sender receives about the receiver’s reaction to the message that has been generated Response and feedback complete the twoway process of communication It is through the feedback that the source.

Sender receiver message channel feedback. 6 The Receiver Send Feedback to the Sender Using the same phases as the sender, the receiver send a message back to the sender providing information on his or her level of comprehension of the message Noises or Barriers to Communication Process. The information may be written or spoken, professional or social, personal or impersonal to name a few possibilities Basically, the communication process involves a sender, receiver, message, channel and feedback However, this simplistic description significantly underrepresents what can actually be a very complex process. Receiver The destination of the message from sender Note Based on the decoded message the receiver gives their feed back to sender If the message distracted by noise it will affect the communication flow between sender and receiver Noise The messages are transferred from encoder to decoder through channel During this process the messages.
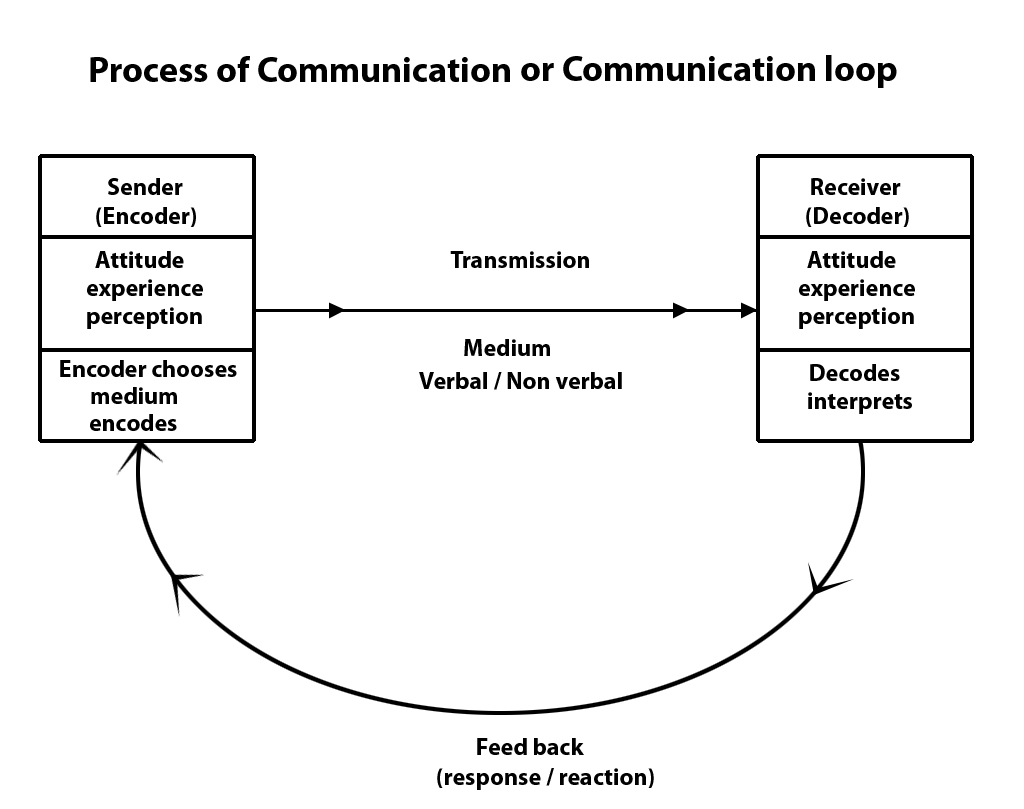
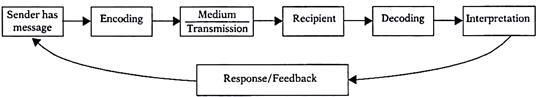
The distortion of the message can happen at any of the stages in communication processsender, receiver, encoding, decoding, channel, message and feedback In order to send our message, it is clear that we need an understanding of the role and function of the communication and audience, and then we select the appropriate channels of communication there will also be feedback from us, as communication, to the audience. The telegraph was a primary means of communicating over distance, prior to widespread use of the telephone, and it had one characteristic that made it completely different from other means of communication One telegraph sent a message to another (sender to receiver) Then, the receiver would become the sender and respond if necessary. The central objective of communication is to transmit meaning The communication process is generally defined in five steps sender has an idea, sender encodes the idea in a message, message travels over a channel, receiver decodes the message, and feedback travels to sender Complete the sentence with the most appropriate choice.
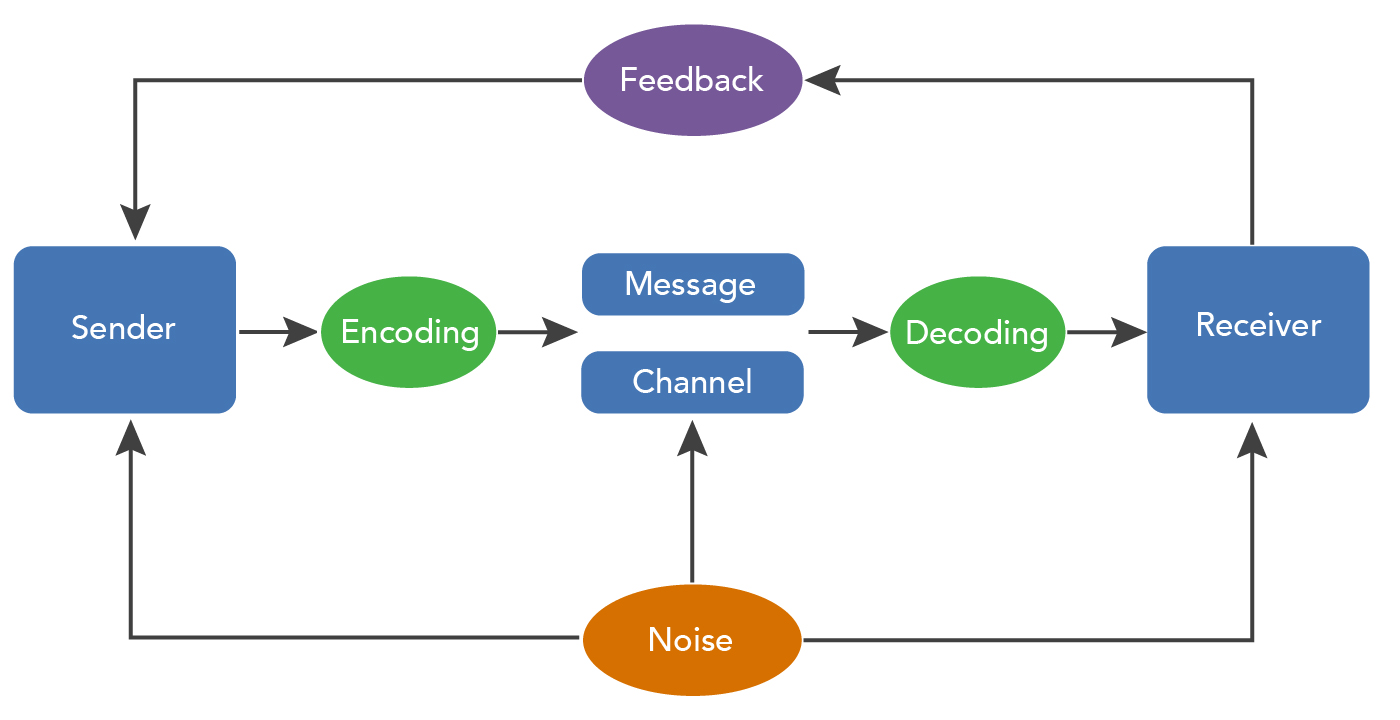
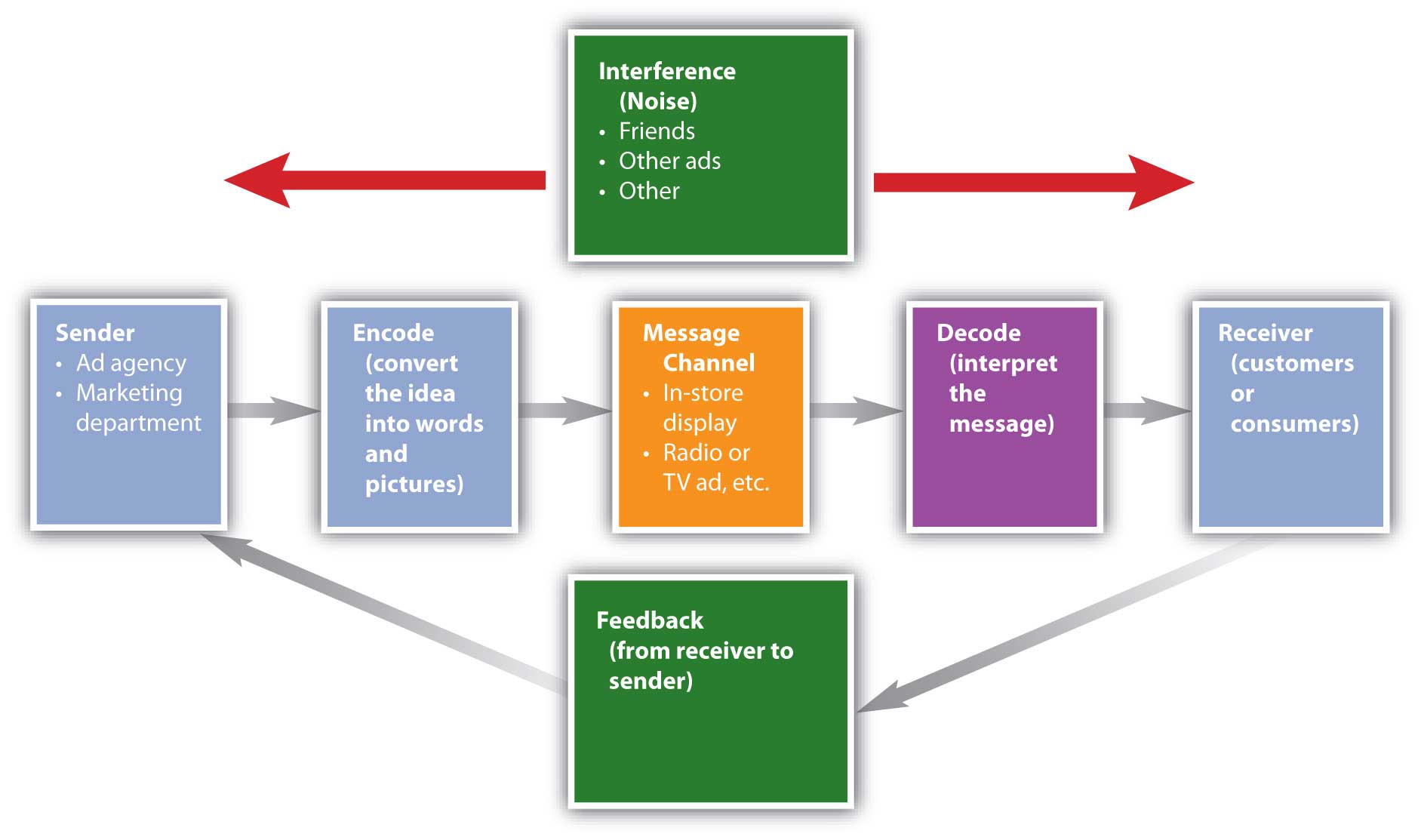
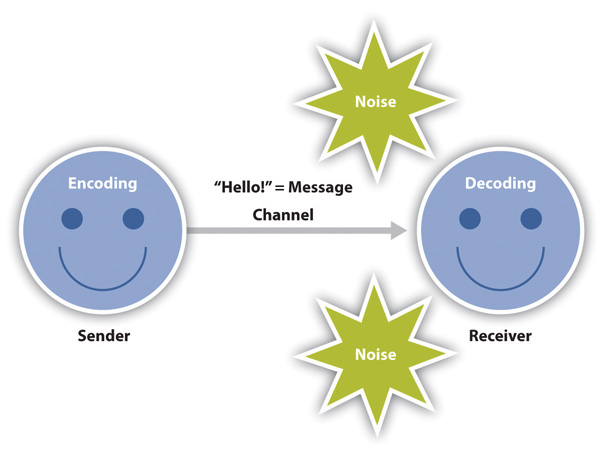
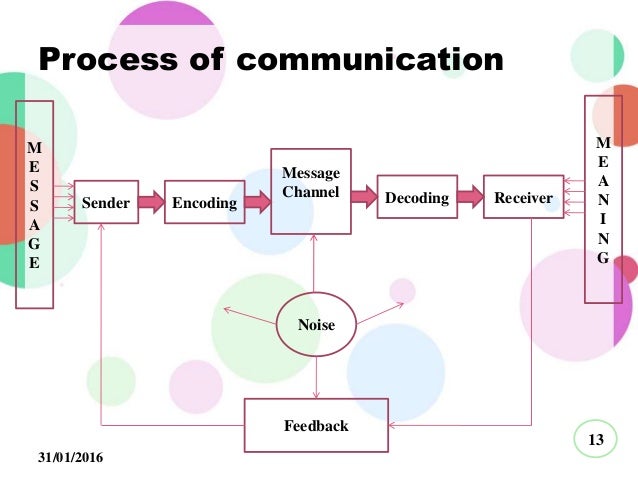
Without feedback, the sender cannot confirm that the receiver has interpreted the message correctly Feedback is a key component in the communication process because it allows the sender to evaluate the effectiveness of the message. Feedback helps the sender know that the message was received and understood Feedback is provided by the receiver and indicates whether or not the message was understood John composes an email message to his boss Sender encodes message Encoding is the conversion of an idea into words or gestures that will convey meaning When John composes a message, he is encoding, or converting an idea. How well they understand the message.
Feedback occurs when the receiver of the message responds to the sender in order to close the communication loop They might respond to let the sender know they got the message or to show the sender Whether they got the message clearly without noise;. A sender can know the effect of his communication only through the feedback ie, response, reaction or interpretation of the message given by the receiver to the sender The receiver encodes the feedback message and sends it back to the sender through some channel The feedback is a vital element in effective communication. If a sender relays a message through an inappropriate channel, its message may not reach the right receivers That is why senders need to keep in mind that selecting the appropriate channel will greatly assist in the effectiveness of the receiver's understanding The sender's decision to utilize either an oral or a written channel for communicating a message is influenced by several factors.
Crystal Jenkins writes a recommendation report Sender has an idea Sender encodes message Feedback travels to sender Receiver decodes message Message travels over channel 2 The Basics of Business Writing Writing in a business environment differs from other types of writing. When the receiver interprets the message;. Treatment is the way in which the message is conveyed to the receiver Treatment also effects the feedback of the receiver Structure The structure of the message or the way it has been structured or arranged, affects the effectiveness of the message Code Code is the form in which the message is sent It might be in the form of language, text, video, etc CChannel Channel is the medium used to send the message.
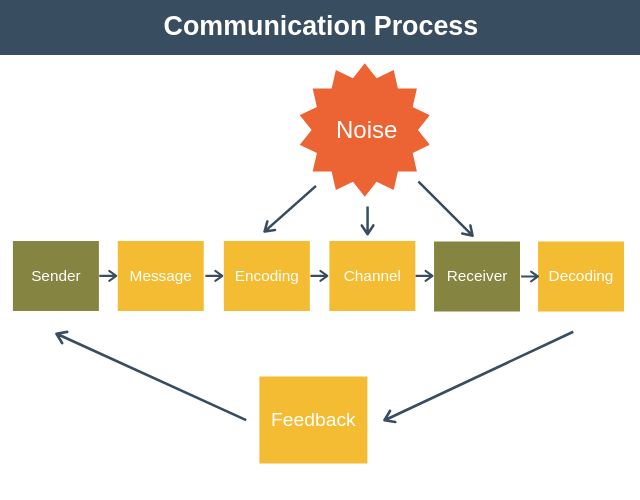
The sender cannot email a message to a receiver who is not computer savvy nor can he write a letter to an illiterate The choice of the medium also depends on the urgency of the message If the sender wants an urgent feed back, he should choose the oral medium You cannot afford to write long memos or letters to a workman on the shopfloor. How well they understand the message. Communication process Sender, Encoding, Message, Channel, Receiver, Decoding, Feedback, Barriers, Context or Situation Learning Objectives To learn about the flow of communication To get familiar with the basic elements of communication process To know what are the barriers and disturbances in communication process.
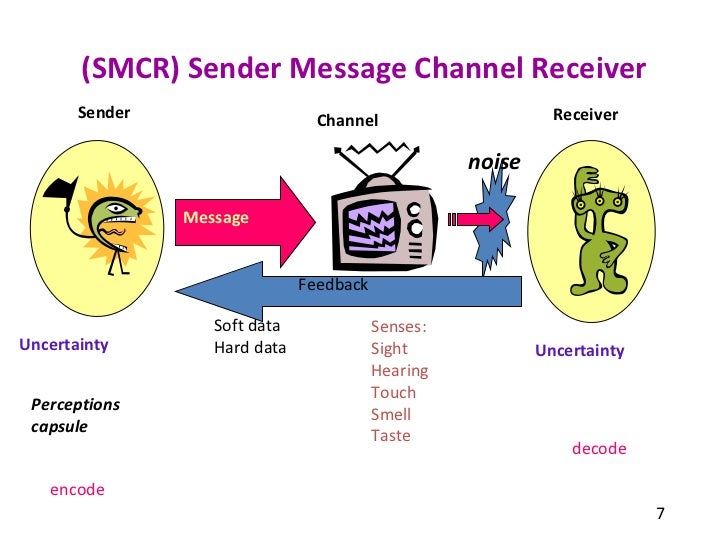
It is important that both the sender and the receiver devote sufficient time exchanging information and feedback respectively Lack of language proficiency Because language is a symbolic means of communication, it creates possibilities of distortion or misunderstanding of the original message. And The receiver must decode the message through the channel that was used Noticeably absent in the SMCR. Feedback Feedback ensures that the receiver understood the message in the way the sender wanted the message to be understood Feedback is also known as reaction and responses The source can judge by the reaction if the message was received correctly Context Context is where the message is received The environment can change the meaning of.
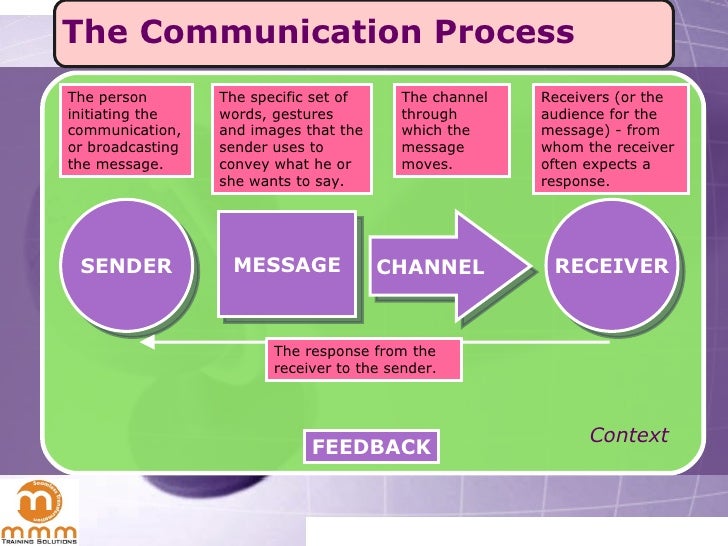
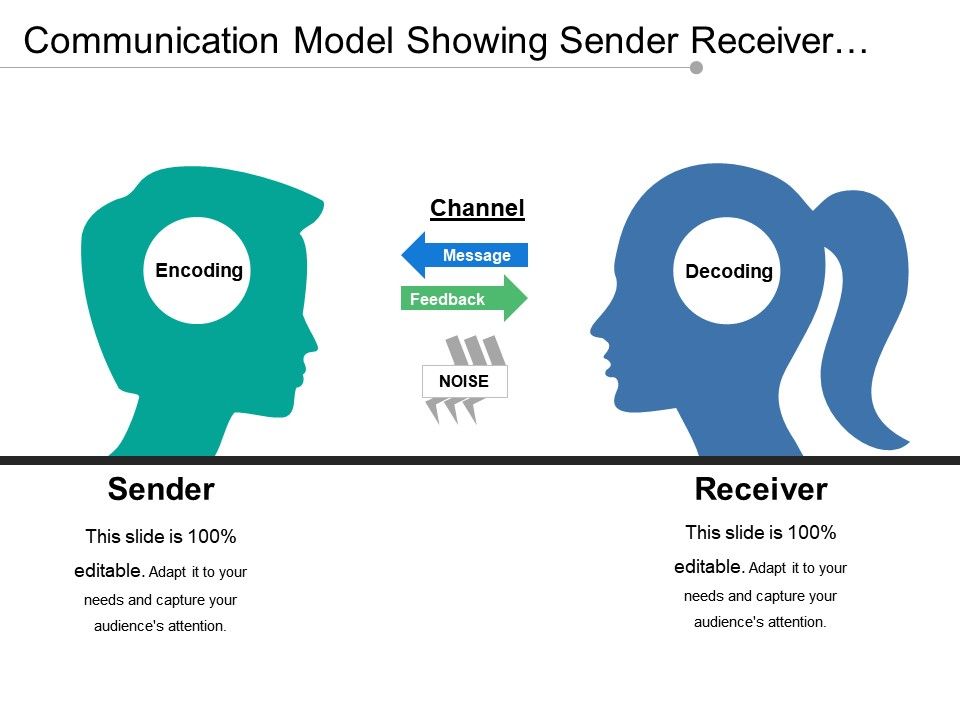
A person who receives and interprets a message Channel The medium or vehicle which facilitates the sender to send a message, such as a letter, email or speaking to someone facetoface Feedback The response of a receiver to a message, such as a comment or a nod of the head;. Communication process Sender, Encoding, Message, Channel, Receiver, Decoding, Feedback, Barriers, Context or Situation Learning Objectives To learn about the flow of communication To get familiar with the basic elements of communication process To know what are the barriers and disturbances in communication process. Feedback The communication process reaches its final point when the message has been successfully transmitted, received, and understood The receiver, in turn, responds to the sender, indicating comprehension Feedback may be direct, such as a written or verbal response, or it may take the form of an act or deed in response (indirect).
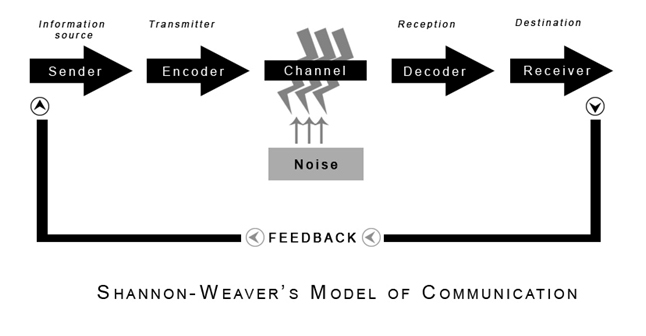
It clarifies the message is understood as intended by the sender. Concepts in Shannon Weaver Model Sender (Information source) – Sender is the person who makes the message, chooses the channel and sends the message Encoder (Transmitter) –Encoder is the sender who uses machine, which converts message into signals or binary data It might also directly refer to the machine Channel –Channel is the medium used to send message. A sender can know the effect of his communication only through the feedback ie, response, reaction or interpretation of the message given by the receiver to the sender The receiver encodes the feedback message and sends it back to the sender through some channel The feedback is a vital element in effective communication.
Thus, the perceptive manager will look for the causes of communication problems instead of just dealing with the symptoms Barriers can exist in the sender, in the transmission of the message, in the receiver, or in the feedback The different barriers of communication are1 Semantic Barriers 2 Psychological Barriers 3 Organisational. A person who receives and interprets a message Channel The medium or vehicle which facilitates the sender to send a message, such as a letter, email or speaking to someone facetoface Feedback The response of a receiver to a message, such as a comment or a nod of the head;. The seven elements in the speech communication process are as follows sender, message, receiver, feedback, channel (or medium), interference and situation All of these elements interact to determine the effectiveness of the communication A change in any one of them is capable of producing a different result.
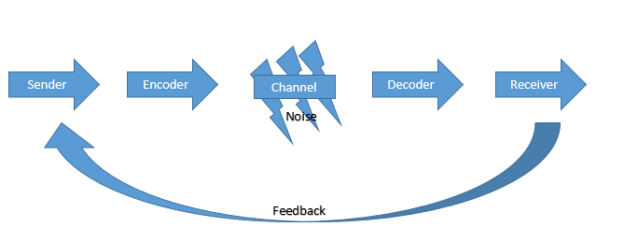
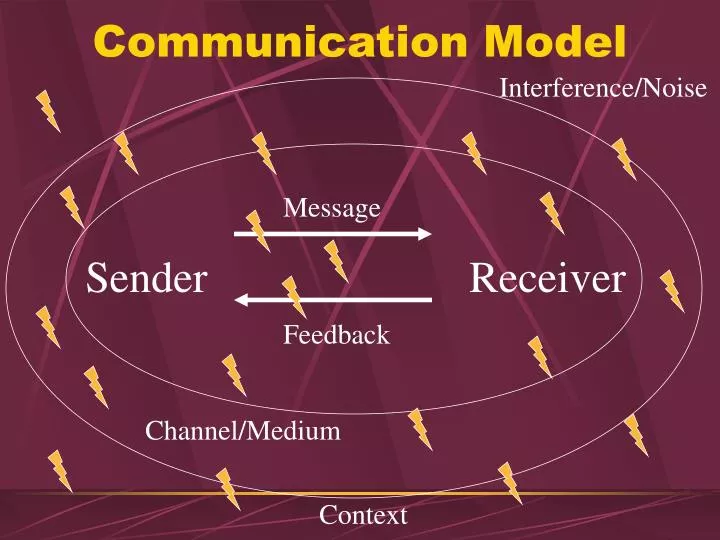
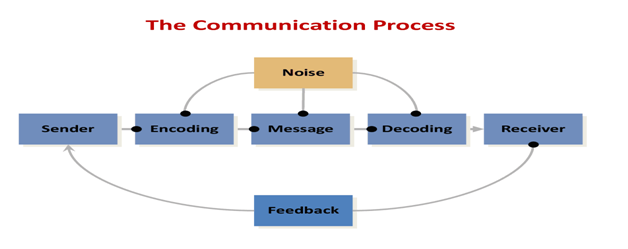
The seven elements in the speech communication process are as follows sender, message, receiver, feedback, channel (or medium), interference and situation All of these elements interact to determine the effectiveness of the communication A change in any one of them is capable of producing a different result. The sendermessagechannelreceiver (SMCR) model of communication is an expansion of the ShannonWeaver model of communicationDavid Berlo created this model, which separated Shannon and Weaver's linear model into clear parts, in 1960 It has been expanded upon by other scholars Berlo described factors affecting the individual components in the communication making the communication more. Concern on the situation than on the message Physical noise can inhibit communication at any point in the process—in the sender, in the message, in the channel, or in the receiver Psychological noise alludes to mechanisms within individuals that restrict a sender’s or receiver’s ability to express and/or understand messages clearly For.
Consists of sender, message, channel, receiver, feedback and context) and have the potential to create misunderstanding and confusion To be an effective communicator and to get our point across without misunderstanding and confusion, our goal should be to lessen the frequency of these problem areas at each stage of this process with. Consists of sender, message, channel, receiver, feedback and context) and have the potential to create misunderstanding and confusion To be an effective communicator and to get our point across without misunderstanding and confusion, our goal should be to lessen the frequency of these problem areas at each stage of this process with. Om 275 guide 23) A receiver’s response to a sender’s message is called A channel B feedback C encoding D decoding 1 BCOM/275 GUIDE 2Click Here to Buythe Tutorial/Answers1) The term channel in communication meansA the medium through which a message travels from sender to receiverB the context of the communicationC the volume at which a message is receivedD the process of changing thoughts into symbols2) This preparation process involves looking at the characteristics of the.
As a result of this model, I will ensure that a strong foundation is established through identifying the sender, channel and receiver within a conversation and removing the possibility of noise Applying these steps will ensure effective communication with future patients. Concern on the situation than on the message Physical noise can inhibit communication at any point in the process—in the sender, in the message, in the channel, or in the receiver Psychological noise alludes to mechanisms within individuals that restrict a sender’s or receiver’s ability to express and/or understand messages clearly For. Feedback It enhances the effectiveness of the communication as it permits the sender to know the efficacy of his message It enables the sender to know if his/her message has been properly comprehended The analysis of feedbacks helps improve future messages Feedback, like the message, can be.
These are sender, ideas, encoding, communication channel, receiver, decoding and feedback We will talk in this article about a specific situation the online communication How we can define communication?. Channel Sender Receiver Feedback Noise Noise Message Transactional Model of Communication • Simultaneous exchange — Msg & Fdbk are integrated into communication to recognize that they occur simultaneously. When does encoding take place?.
A person who receives and interprets a message Channel The medium or vehicle which facilitates the sender to send a message, such as a letter, email or speaking to someone facetoface Feedback The response of a receiver to a message, such as a comment or a nod of the head;. Feedback Response from the receiver used to decide whether clarification is necessary and to determine whether the message sent is the message received Repeating, restatement, examples, questions. It clarifies the message is understood as intended by the sender.
It clarifies the message is understood as intended by the sender. – Once the message is completely decoded, the receiver has to begin formulating the feedback – With this step, the receiver becomes the sender, and has to apply the same clarity of thought while formulating the feedback – The correct channel of communication must be chosen to send the feedback, and it must reach the sender on time. The information may be written or spoken, professional or social, personal or impersonal to name a few possibilities Basically, the communication process involves a sender, receiver, message, channel and feedback However, this simplistic description significantly underrepresents what can actually be a very complex process.
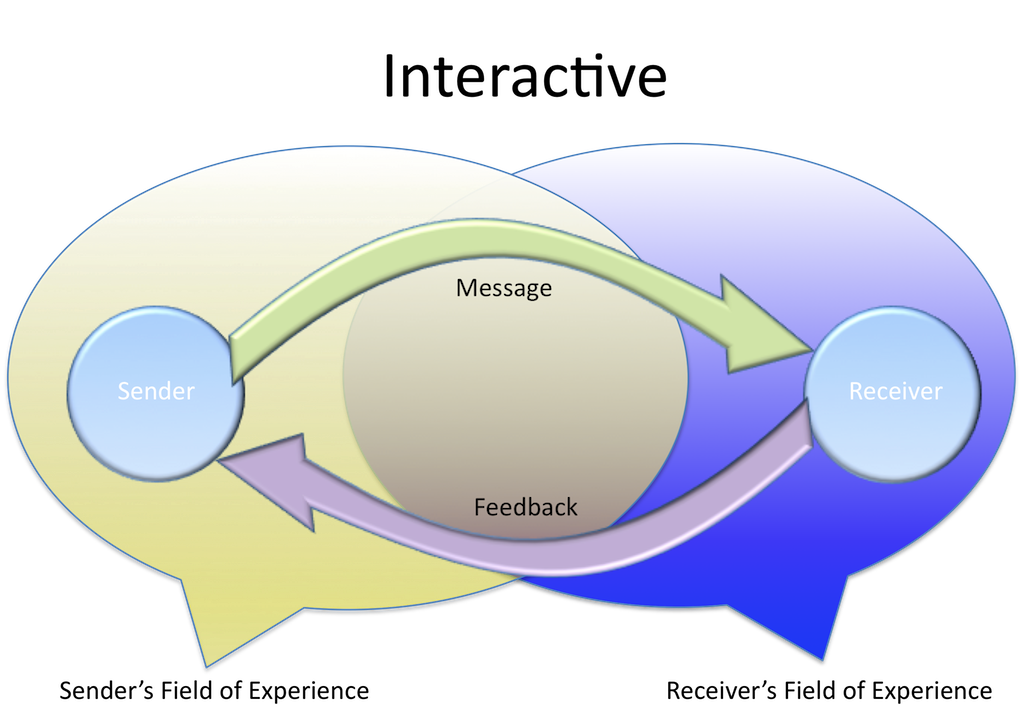
Feedback The Feedback is the final step of the process that ensures the receiver has received the message and interpreted it correctly as it was intended by the sender It increases the effectiveness of the communication as it permits the sender to know the efficacy of his message The response of the receiver can be verbal or nonverbal Note. Receiver “The receiver receives the message from the source, analyzing and interpreting the message in ways both intended and unintended by the source” (McLean, 05) Feedback When you respond to the source, intentionally or unintentionally, you are giving feedback Feedback is composed of messages the receiver sends back to the source. Communication is a process that concerns an exchange of ideas and facts between two or more entities, to achieve a mutual idea The.
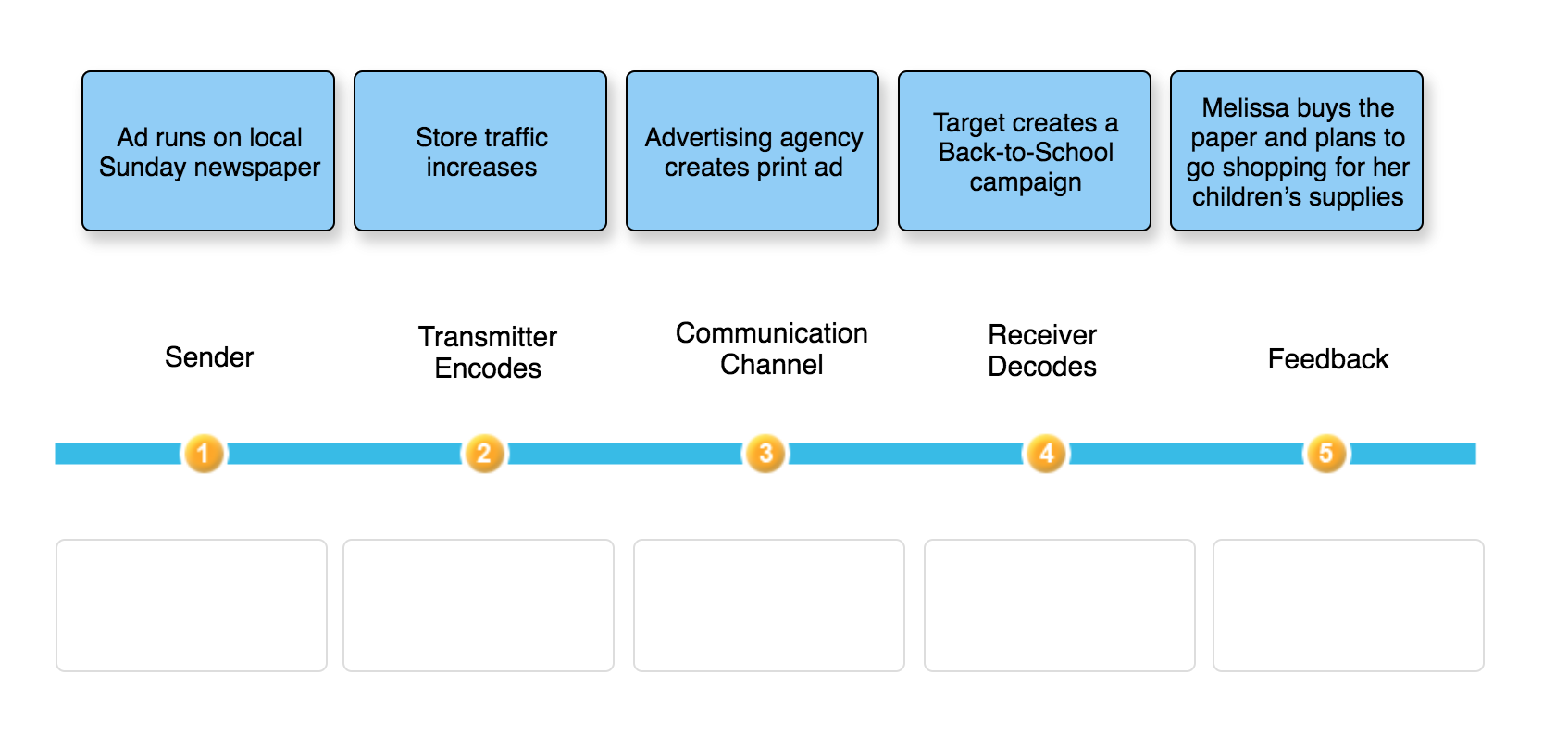
He usually gives feedback to the sender in order to make sure that the message was properly received Noise the message, transferred through a channel, can be interrupted by external noise (for instance, conversation may be interrupted by thunder or crowd noise) Feedback The receiver can get an inaccurate message This is why feedback from the receiver is important in case the message is not properly received. A message channel is a term that refers to the medium that carries the message from the sender to the receiver In marketing/promotions the message channel may be television, radio, newspaper, or a sales person The Receiver Anyone who is audience to the message is referred to as the receiver For example, all viewers of a television advertisement can be referred to as the ‘receivers’ of the message Decoding When the receiver views or hears the message they do what is termed. The components or elements of the Business Communication Process are ornately explained under with the help of a fantasy television advertisement Unilever Bangladesh Ltd of Lux Soap Elements of Communication Process Sender Sender is the person or party who sends the message or idea to the receiverSender is the source of any communication and communication takes place based on him in our.
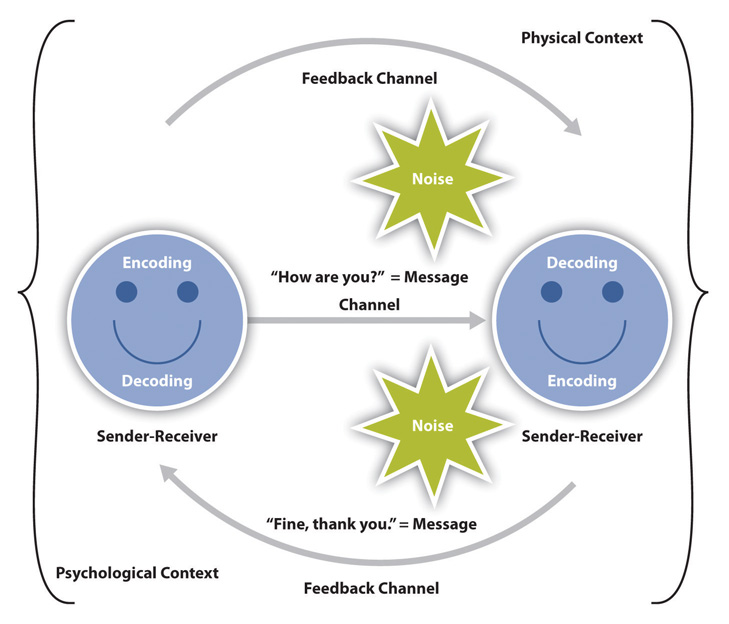
As a result of this model, I will ensure that a strong foundation is established through identifying the sender, channel and receiver within a conversation and removing the possibility of noise Applying these steps will ensure effective communication with future patients. It is two linear models stacked on top of each other The sender channels a message to the receiver and the receiver then becomes the sender and channels a message to the original sender This model has added feedback, indicating that communication is not a one way but a two way process. The interaction model of communication describes communication as a process in which participants alternate positions as sender and receiver and generate meaning by sending messages and receiving feedback within physical and psychological contexts (Schramm, 1997) Rather than illustrating communication as a linear, oneway process, the.
He responds Paige is the sender, the question is the message, and Bill is the receiver and gives Paige feedback by answering the question Myriad areas and ways exist where problems could arise even in this short exchange If Paige whispers, Bill might not hear it. More complex models throw in a fourth element the channel via which the message is sent The most advanced communication models include a fifth element feedback, that is, a return message sent from the receiver back to the sender Feedback could be as formal as handing out a presentation evaluation following your speech or presentation. The telegraph was a primary means of communicating over distance, prior to widespread use of the telephone, and it had one characteristic that made it completely different from other means of communication One telegraph sent a message to another (sender to receiver) Then, the receiver would become the sender and respond if necessary.
When both sender and receiver need to exchange. Receiver The destination of the message from sender Note Based on the decoded message the receiver gives their feed back to sender If the message distracted by noise it will affect the communication flow between sender and receiver Noise The messages are transferred from encoder to decoder through channel During this process the messages. Receiver The receiver is one who is intended to receive the message sent by sender Feedback Feedback constitutes the information which the sender receives about the receiver’s reaction to the message that has been generated Response and feedback complete the twoway process of communication It is through the feedback that the source.
The last part of decoding is “responding to a source’s message,” when the receiver encodes a message to send to the source When a receiver sends a message back to a source, we call this process feedback Schramm talks about three types of feedback direct, moderately direct, and indirect (Schramm, 1954) The first type, direct feedback, occurs when the receiver directly talks to the source. The seven elements in the speech communication process are as follows sender, message, receiver, feedback, channel (or medium), interference and situation All of these elements interact to determine the effectiveness of the communication A change in any one of them is capable of producing a different result. Feedback occurs when the receiver of the message responds to the sender in order to close the communication loop They might respond to let the sender know they got the message or to show the sender Whether they got the message clearly without noise;.
It is the response or reaction given by the receiver to the sender of the message Sender;. It is two linear models stacked on top of each other The sender channels a message to the receiver and the receiver then becomes the sender and channels a message to the original sender This model has added feedback, indicating that communication is not a one way but a two way process. Encoding happens on the sender's end, involving the way in which the message is transmitted;.
More complex models throw in a fourth element the channel via which the message is sent The most advanced communication models include a fifth element feedback, that is, a return message sent from the receiver back to the sender Feedback could be as formal as handing out a presentation evaluation following your speech or presentation. Concern on the situation than on the message Physical noise can inhibit communication at any point in the process—in the sender, in the message, in the channel, or in the receiver Psychological noise alludes to mechanisms within individuals that restrict a sender’s or receiver’s ability to express and/or understand messages clearly For.
/what-is-communication-process-1689767_FINAL-069d65e4e1414e5c917379c42a537a66.png)
The Basic Elements Of The Communication Process
Ppt The Communications Process Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Models Of Communication Wikipedia
Sender Receiver Message Channel Feedback のギャラリー

Technology And The Communication Process

Sender Channel Receiver Communication In Health Eportfolio
The Communication Modelkidcourses Com

Interpersonal Communication

6 Model Model Describes What Is Necessary For An Act Of Communication To Take Place A Model Represents The Major Features And Eliminates The Unnecessary Details Of Communication Functions Of Communication Models To Clarify The Scope Of Human

Unit 1 Communication Process

Exe
What Is Communication

Process Of Communication Mass Communication And Media

What Is Communication Process Definition And Meaning Business Jargons

Kerwinoctavo

The Communication Process Getting Your Messages Heard Ezanga Blog Ezanga Com

Language Barriers To Effective Communication

Mindful Communication Parks Rec Business Magazine Prb

The Process Of Communication Organizational Behavior And Human Relations
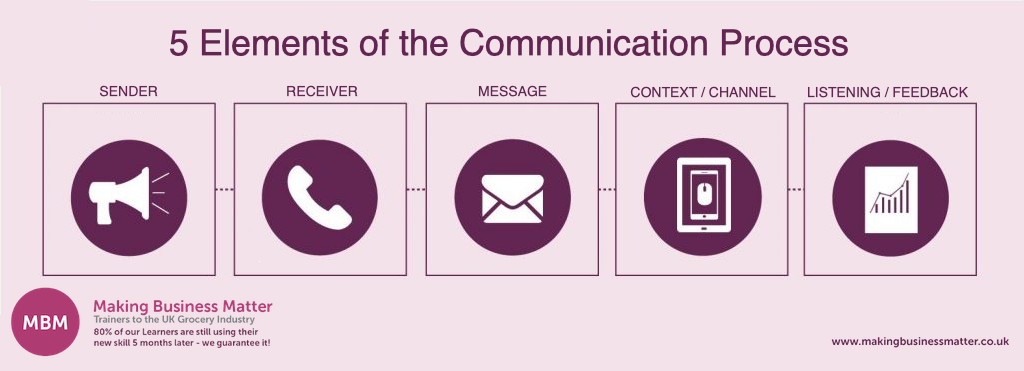
The Ultimate Guide To Communication Skills By Making Business Matter Mbm Medium

A Model Of Communication
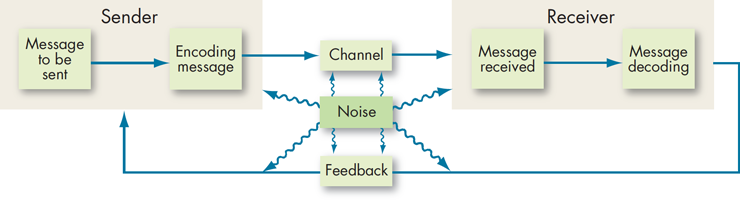
Solved Using The Communication Process From Your Reading Chegg Com

The Process Of Communication Organizational Behavior And Human Relations

Communication Sender Channel Receiver Communication In Physiotherapy

Non Technical Skills Pre Course Package For Hedsup Course Ppt Download
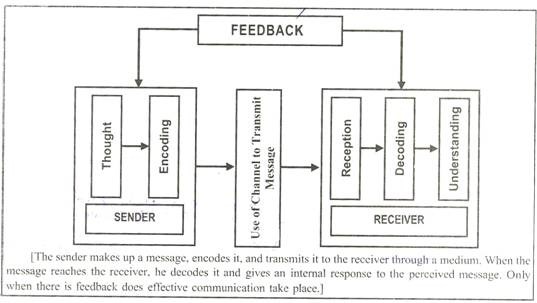
Process Elements Of Communication Professional Shiksha

Theory Concept Of Communication Message Channel From Sender To Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image

1 Communication Theory Sender Channel Receiver Communication In Occupational Therapy
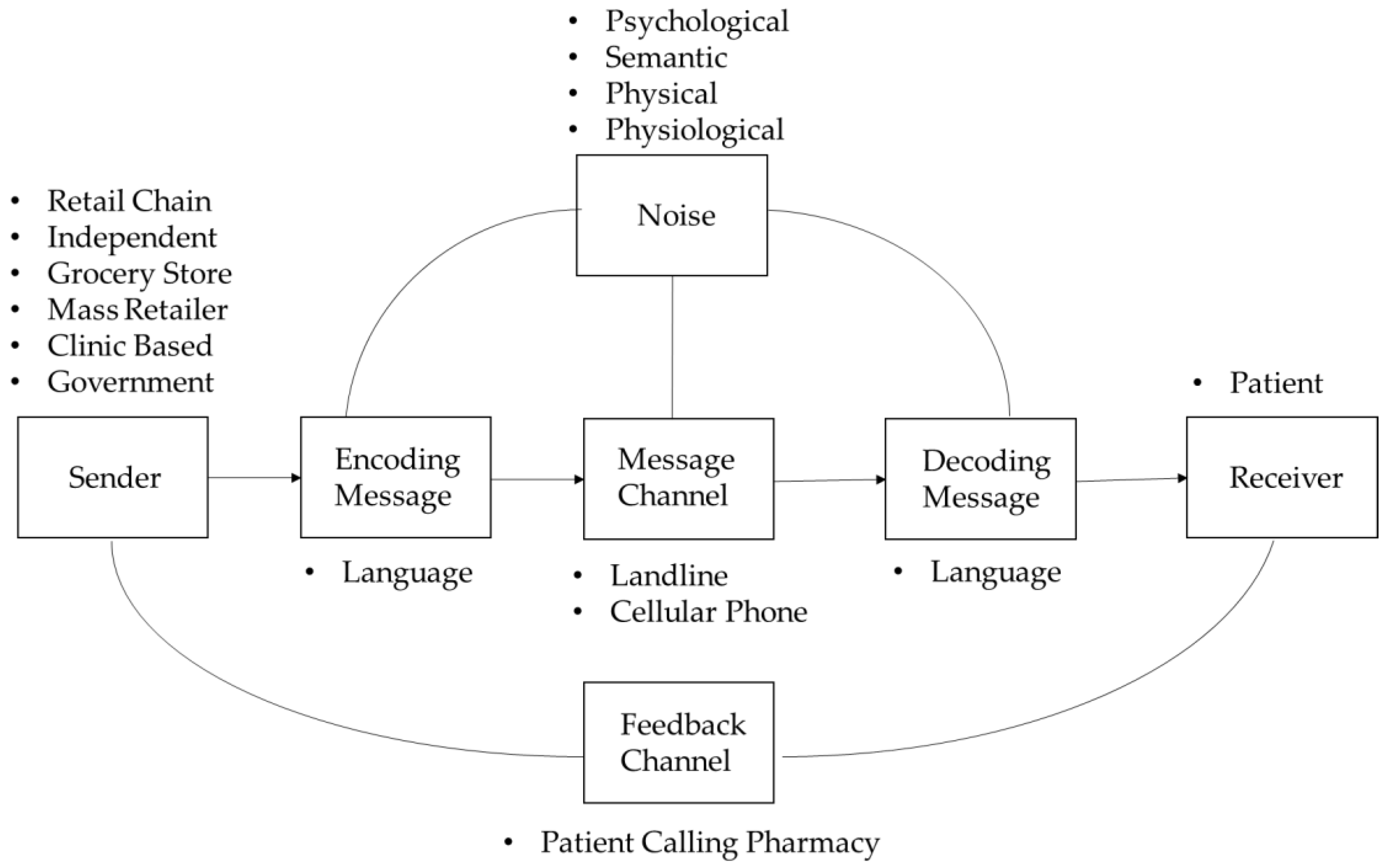
Pharmacy Free Full Text Uncertainty And Motivation To Seek Information From Pharmacy Automated Communications Html

D4e1 Communication Process

Language Barriers To Effective Communication

Process Of Communication Word Search Wordmint

Teresa And Gaby S Communication Theory Communication Theories And Libraries
Communication

6 Model Model Describes What Is Necessary For An Act Of Communication To Take Place A Model Represents The Major Features And Eliminates The Unnecessary Details Of Communication Functions Of Communication Models To Clarify The Scope Of Human
Communication Theory
Feedback In Communication Or Meaning Of Feedback Business Consi
The Process Of Communication Organizational Behavior And Human Relations
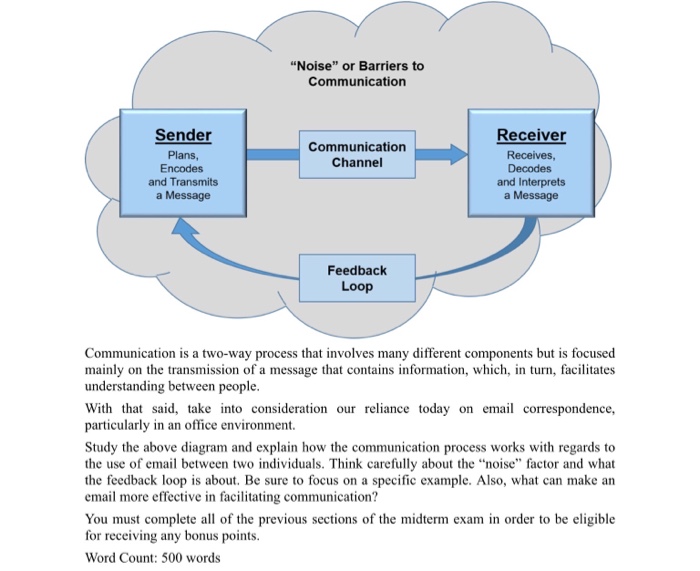
Noise Or Barriers To Communication Sender Plans Chegg Com
Factors Influencing The Promotion Mix Communication Process And Message Problems

Communication Model Showing Sender Message Channel Receiver And Feedback Powerpoint Slide Clipart Example Of Great Ppt Presentations Ppt Graphics
Communication Skills
Ppt Communication Model Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Solved The Communication Process The Communication Proces Chegg Com

Models Of Communication Wikiwand
3 Models Of Communication

Effective Communication Quick Guide Tutorialspoint

Communication Theory Sender Channel Receiver Communication In Physiotherapy

Business Communication Soft Skills Sample Questions Communication Psychology
Communication Loop The Process Of Communication

What Is Communication Please Get Ready To Take Notes Ppt Download

Communication Model Showing Sender Message Channel Receiver And Feedback Powerpoint Slide Clipart Example Of Great Ppt Presentations Ppt Graphics
The Communication Process

Organizational Behavior Chapter 14 Flashcards Quizlet
Q Tbn And9gcqpzwdlycxwe2zy 7y4c9ibsfyafo1ulf9isrgg8hjhx0 9i3i Usqp Cau

Berlo S Smcr Model Of Communication Businesstopia
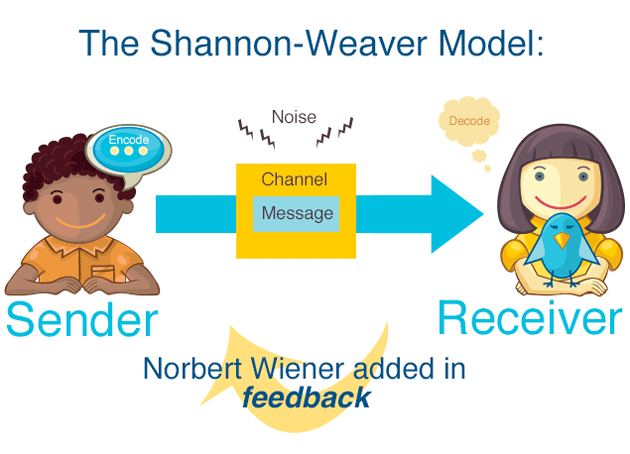
Shannon And Weaver Model Of Communication
A Practical Definition Of Communication A Model For Project Managers

Communication Model Assignment Objective Students Chegg Com

Role Of The Sender In Communication Process Ifioque Com
Communication

om 275 Guide 23 A Receiver S Response To A Sender S Message Is Cal

Introduction To Academic Communication Cssc Ppt Download

Elements Of Communication 1
Communication Process Docx
002 What Is Communication Explain Communication Process B Com Ii Semester All Notes
Communication Model Showing Sender Receiver Channel Feedback Powerpoint Slide Images Ppt Design Templates Presentation Visual Aids

Geektieguy Why Agile Software Development Works

Communicating Requirements Effectively Communications Model

Intranets Extranets And Private Exchanges Communication Sender Message Channel Receiver Feedback Context Communication Process Effective Communication Ppt Download
Communication Process Business Basics
How The Communication Process Works Communication Training

The Advertising Communication System Studiousguy

Transmission Model Of Communication Melisa Nahimana Ppt Download

Communication Model Having Sender Message Channel And Receiver Presentation Powerpoint Templates Ppt Slide Templates Presentation Slides Design Idea

The Encode Decode Model Of Communication

Analyze And Discuss Love Cuts 割爱 Com101a S Blog

Sender Message Channel Receiver Model Of Communication Definition Application Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Sender Powerpoint Templates Ppt Slides Images Graphics And Themes

om 275 Guide 1 1 A Receiver S Response To A Sender S Message Is Ca
The Communication Process

Delivery

Communication And Consumer Behavior Ppt Video Online Download
Process Of Communication
Vussc Content Tourism Applying Effective Communication Skills The Process Of Communication Wikieducator
Communication Model Message Sender Receiver Feedback Decode Encode Ppt Video Online Download
Management And Business English Communication Process Model An Interpersonal Perspective

Decoding Powerpoint Templates Slides And Graphics
Chapter 1 Introducing Communication The Evolution Of Human Communication From Theory To Practice

Communication What Is It The Definition For This Class A Process By Which Information Is Exchanged Between Individuals Through A Common System Of Ppt Download
Q Tbn And9gcress7hsnkn8mnnsjzixhoajpqmbu1la2yzojjcaubeiu7d3cti Usqp Cau
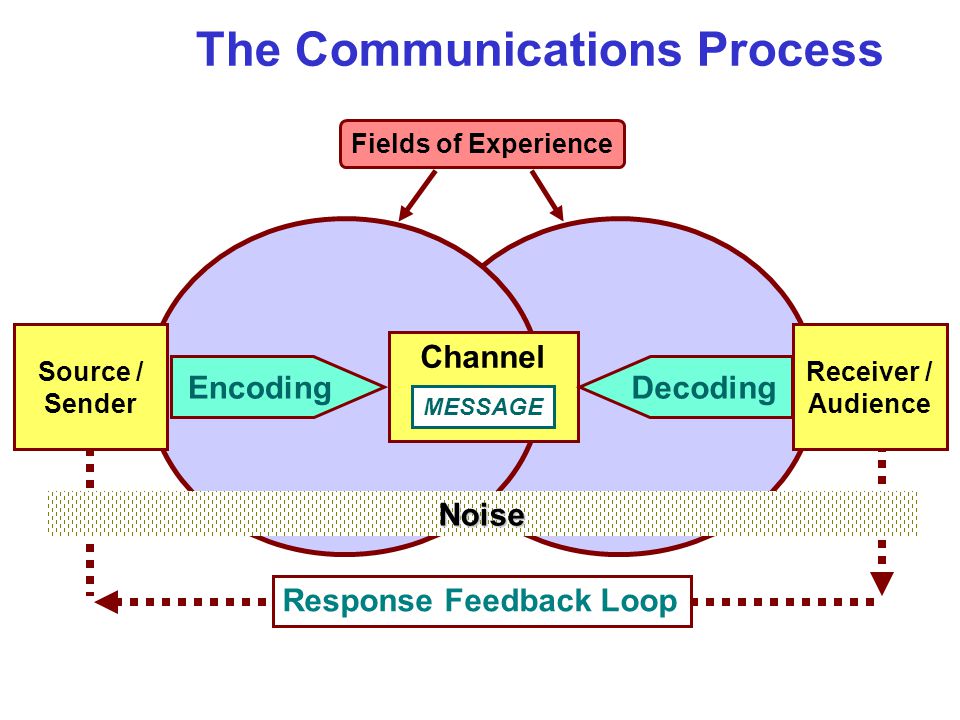
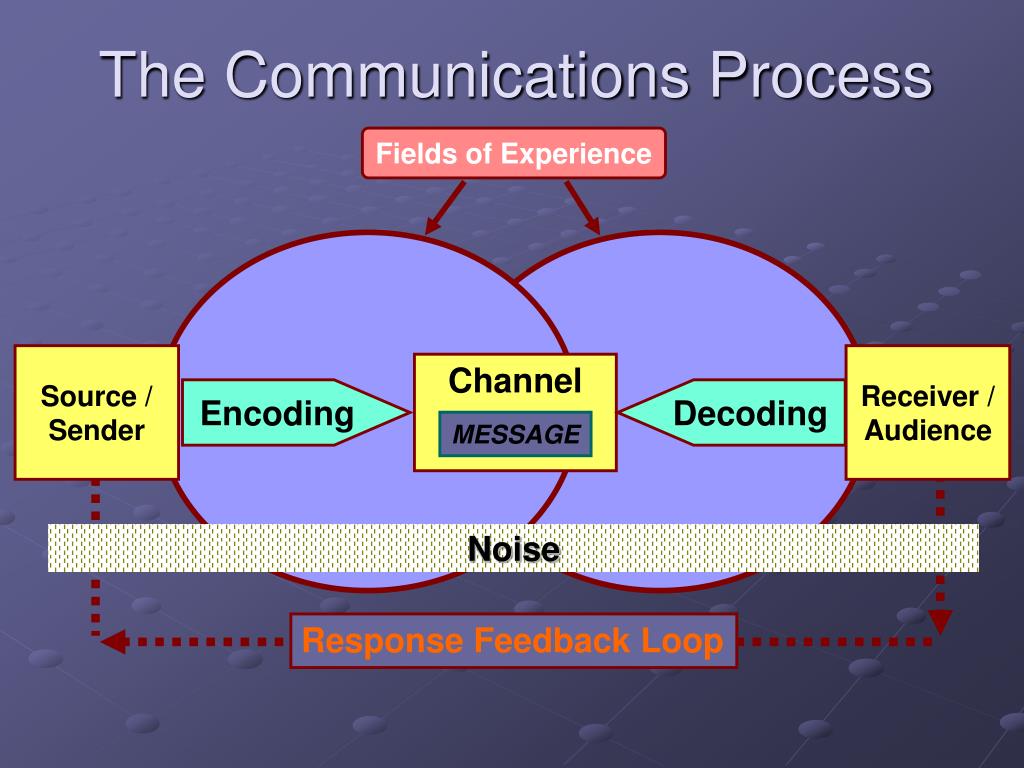
Fields Of Experience The Communications Process Response Feedback Loop Channel Message Decoding Receiver Audience Source Sender Encoding Noise Ppt Download

Broadcasting Archives Educational Website For Online Learning
Q Tbn And9gctkoxs3zd Jae8w Itmnczmgsi6hn6m7w0jiq Sj8awudq4vmwk Usqp Cau

Communication Model Showing Sender Message Channel Receiver And Feedback Powerpoint Slide Clipart Example Of Great Ppt Presentations Ppt Graphics
Www Studocu Com Row Document Makerere University Business Communication Lecture Notes Communication Lecture Notes 1 View

Business Communication 15
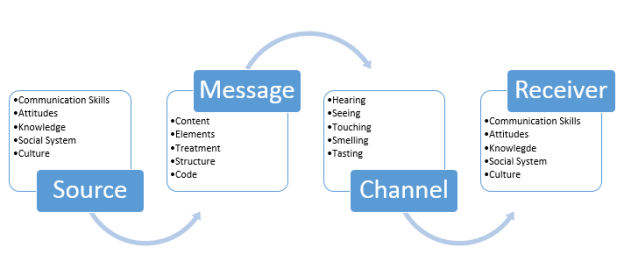
Communication Theory

Communication And Management Principles Of Management

The Process Of Communication Chapter 2 Communication Model Sender Message Receiver Feedback Ppt Download
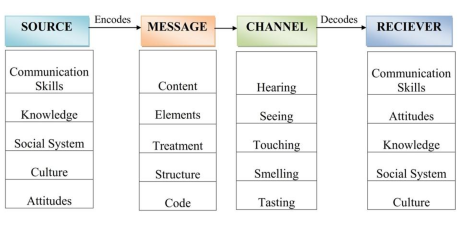
Communication Models Linear Interactive And Transactional Model Simple And Comprehensive Notes Only On Simplinotes

3 Ways To Choose A Powerful And Effective Communication Style Doncrawley Com
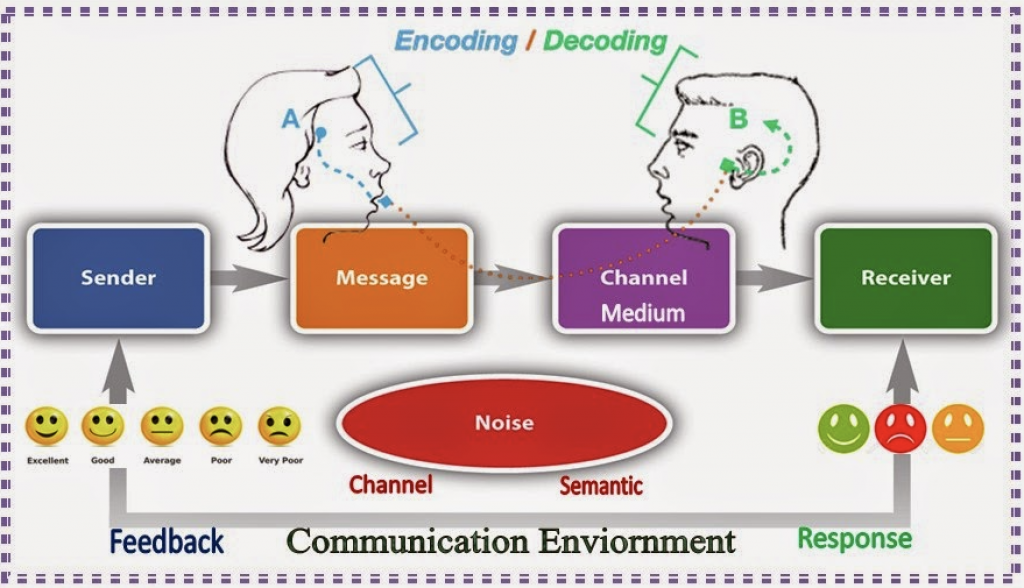
I Didn T Hear You Community Govloop

1 Communication Theory Sender Channel Receiver Communication In Paramedicine



