Marginale Gingiva Definition
2 = mild inflammation, such as the preceding criteria, in all portions of gingival marginal or papillary;.

Marginale gingiva definition. Tooth surface on one side and free or marginal gingiva on the other Junctional epithelium lines the base (bottom) and aids gingival fibers in attaching the gingiva to the tooth (Definition) All of the keratinized gingiva apical to the bottom of the sulcus Definition attached gingiva Term. Gingival pigmentation is a discoloration of the gingiva due to a variety of lesions and conditions associated with several endogenous and exogenous etiologic features It may range from physiologic reasons (eg racial pigmentation) to manifestations of systemic illnesses (eg Addison's disease) to malignant neoplasms (eg melanoma and. 1 = mild inflammation or with slight changes in color and texture but not in all portions of gingival marginal or papillary;.
Plural gingivae (jĭn′jəvē′) The gums of the mouth The gingiva are made up of epithelial tissue that is attached to the bones of the jaw and surrounds and supports the bases of the teeth Also called gum 2 The American Heritage® Science Dictionary Copyright © 11. Gingival fibers and periodontitis Gingival fibers help to protect against periodontitis Once they are compromised, they cannot be regenerated When the gingival fibers are destroyed, the gingival sulcus. Define gingival margin gingival margin synonyms, gingival margin pronunciation, gingival margin translation, English dictionary definition of gingival margin n 1 An edge and the area immediately adjacent to it;.
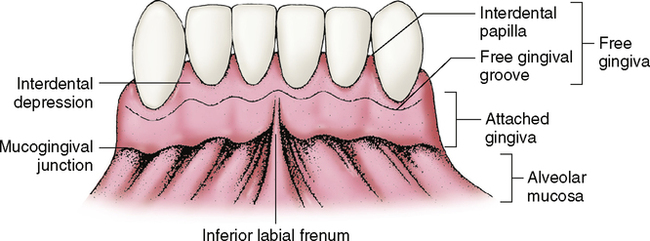
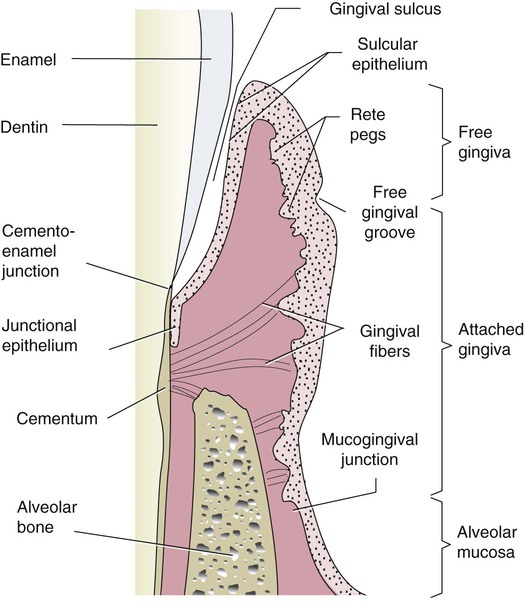
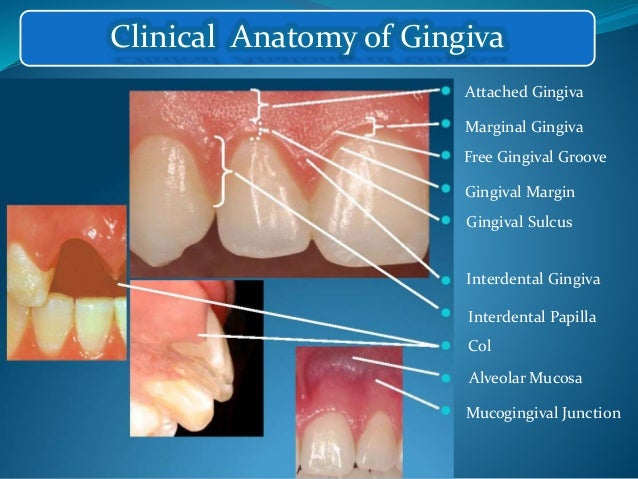
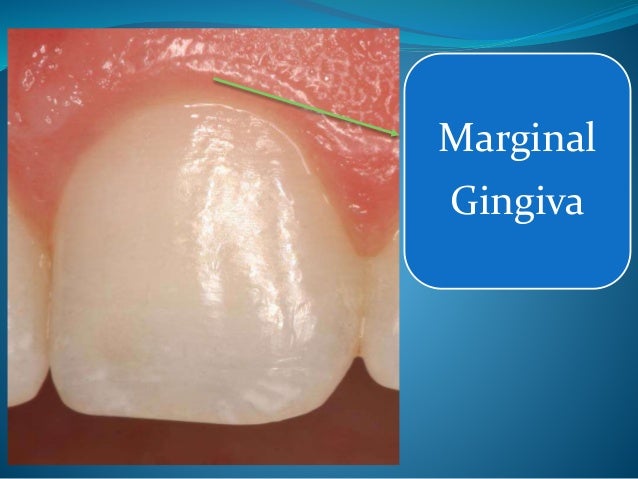
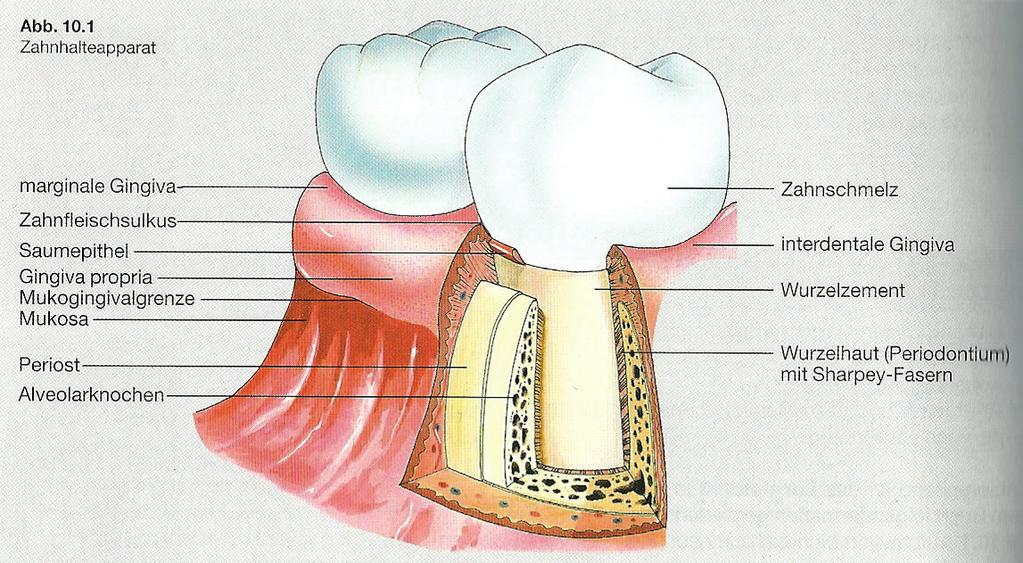
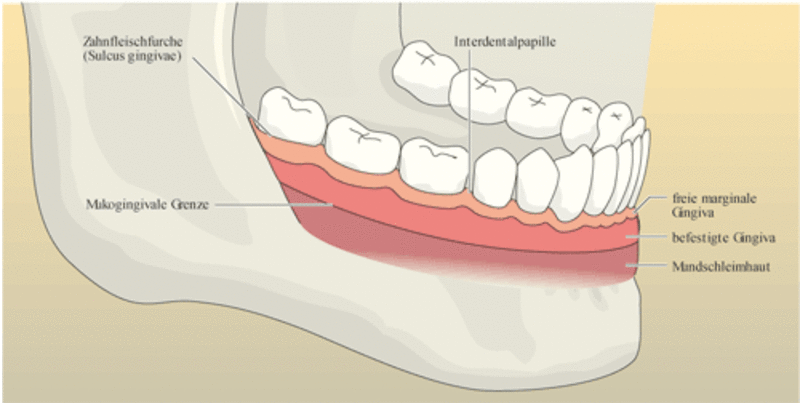
The gingiva is divided anatomically into marginal, attached and interdental areas Marginal gingiva The marginal gingiva is the terminal edge of gingiva surrounding the teeth in collar like fashion In about half of individuals, it is demarcated from the adjacent, attached gingiva by a shallow linear depression, the free gingival groove. Marginal gingiva The marginal gingiva is the terminal edge of gingiva surrounding the teeth in collar like fashion In about 50% of individuals, it is demarcated from the adjacent, attached gingiva by a shallow linear depression, the free gingival groove Usually about 1 mm wide, it forms the soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus. Gingival sulcus A shallow space between the marginal gingiva and the external tooth surface is termed as gingival sulcus The boundaries of the gingival sulcus are, Inner Tooth surface which may be the enamel, cementum, or a part of each, depending on the position of the junctional epithelium Outer Sulcular epithelium.
Gingiva is the scientific term for our Gums Yes, the pinkish transparent tissues in our oral cavity hold onto the tooth DefinitionThe Gingiva is the part of the oral mucosa that covers the alveolar processes of the jaws and surrounds the necks of the teethColourThe colour of the Gingiv a is usually coral Pink in colourThe colour varies among different individuals. Marginal gingiva The marginal gingiva is a 15 mm strip of gingival tissue which surrounds the neck of the tooth and is known as such due to the fact that the inner wall forms the gingival wall of the sulcus. A fissure in the gingival tissues and is usually caused by traumatic oral hygiene, abnormal frenula, trauma from occlusion, orthodontic, or pierce related trauma.
Biofilm forms at the gingival margin of the sinus tract and leads to marginal periodontitis When plaque or calculus is encountered upon probing, the treatment and prognosis of the tooth are altered;. Home / medterms medical dictionary az list / oral health center / gingiva definition Medical Definition of Gingiva Medical Author Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD. The marginal gingiva has a more translucent appearance than the attached gingiva, yet has a similar clinical appearance, including pinkness, dullness, and firmness In contrast, the marginal gingiva lacks the presence of stippling, and the tissue is mobile or free from the underlying tooth surface, as can be demonstrated with a periodontal probe.
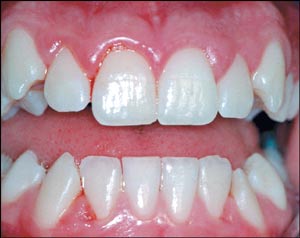
The excessively detailed stippled surface texture of the base area (false gums) can be observed, mimicking the physiologic stippling of gum tissue in nature Note how there is minimal to no stippling on the marginal gingiva, which is the millimeter or so of pink immediately adjacent to the teeth. At the outer or lower limits;. The definition of gingival recession is the displacement of the marginal tissue apical to the cementoenamel junction Orthodontic treatment may promote the development of recessions possibly by positioning the root close to or outside alveolar cortical plates and this, associated to poor hygiene can lead to periodontal breakdown.
The marginal Gingiva or unattached Gingiva is the terminal edge or border of the Gingiva that surrounds the teeth in a collarlike fashion The marginal Gingiva is usually about 1mm wide, and it forms a soft tissue wall of the gingival sulcus It may be separated from the tooth surface with a periodontal probe. 3 = moderate, bright surface inflammation, erythema, edema and/or hypertrophy of gingival marginal or papillary;. A A large fibrous epulis on maxillary gingivab Widespread fibrous gingival enlargement on a patient on cyclosporine therapyc Histological image of a nodule of fibrous hyperplasia of the gingiva (H&E, Overall magnification × ) In this case, the collagen varies from superficially hyalinised to more edematous in deeper tissues d Histological image showing large stellate fibroblasts in a.
Ballooning of interdental papilla and/or marginal gingiva Gingiva is red or bluish/red, soft and friable with smooth shiny surface and bleeds easily May be generalized or localized Caused by prolonged exposure to plaque. A border See Synonyms at border 2 The blank space bordering the written or printed area on a page. Marginal Gingiva The portion that is unattached to underlying tissues and helps to form the sides of the gingival crevice;.
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen, red, and may bleed In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. The tooth now requires both endodontic and periodontal treatments. 1 any of various viscid, amorphous exudations from plants, hardening on exposure to air and soluble in or forming a viscid mass with water 2 any of various similar exudations, as resin 3 a sticky, adhesive preparation of such a plant substance, as for use in the arts or bookbinding 4 chewing gum.
Gingivitis is a nondestructive type of periodontal disease, but untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitisThis is more serious and can eventually lead to loss of teeth. The gingiva is composed of an outer epithelium and an inner network of connective tissue This outer epithelial layer is keratinized, forming a protective layer around the tooth Contained within the inner gingival connective tissue are gingival fibroblasts, which play a crucial role in tissue repair and the inflammatory response. Marginal Gingiva – Not Stippled Attached Gingiva is bound to underlying alveolar bone, not the freely movable alveolar mucosa Where is Stippling seen Microscopically ?.
A A large fibrous epulis on maxillary gingivab Widespread fibrous gingival enlargement on a patient on cyclosporine therapyc Histological image of a nodule of fibrous hyperplasia of the gingiva (H&E, Overall magnification × ) In this case, the collagen varies from superficially hyalinised to more edematous in deeper tissues d Histological image showing large stellate fibroblasts in a. Early stage characterized by violaceous marginal gingiva More advanced lesions become necrotic and covered by a pseudomembrane containing fungal hyphae Aspergillus spp Oral involvement is commonly secondary to more serious systemic infection 33 In the late stage, the lesions may progress and include destruction of the alveolar bone and. Normal Clinical Features Gingiva is divided into Oral part Vestibular part Anatomically, it has been divided into MARGINAL gingiva ATTACHED ginigiva Pyramidal INTERDENTAL gingiva Col A Marginal gingiva / Free gingiva / Margio Gingivalis Definition It is the terminal edge or border of the gingiva surrounding the teeth like a collar.
Gingiva become inflamed (gingivitis) The longer that plaque and tartar remain on your teeth, the more they irritate the gingiva, the part of your gum around the base of your teeth, causing inflammation In time, your gums become swollen and bleed easily Tooth decay (dental caries) also may result If not treated, gingivitis can advance to. Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen, red, and may bleed In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Definition The flowing of blood from the marginal gingival area, particularly the sulcus, seen in such conditions as GINGIVITIS, marginal PERIODONTITIS, injury, and ASCORBIC ACID DEFICIENCY do not confuse with BLEEDING ON PROBING, GINGIVAL see PERIODONTAL INDEX Other names Hemorrhage, Gingival;.
Gingival recession is defined as an apical shift of the gingival margin (GM) from its position 1 mm coronal to or at the level of the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) with exposure of the root surface to the oral environment The displacement of marginal tissue apical to the cemento enamel junction (CEJ). Stefan A Hienz, Sašo Ivanovski, in Functional Occlusion in Restorative Dentistry and Prosthodontics, 16 Epithelium of the Gingiva Normal gingiva covers the alveolar bone and tooth root to a level just coronal to the cementenamel junction At the dentogingival junction, the marginal, or unattached, gingiva is the terminal edge of the gingiva, surrounding the teeth in a collarlike fashion. Fibrotic gingiva is described as “hyperkeratinized tissue with an abnormal whitish thickening of the keratin layer of the epithelium” 1 The problem is that, at first glance, it appears light in color and “firm” to the touch In reality, it appears light because of the lack of blood flow and constricted blood vessels.
Gingival hyperplasia is a localized or generalized, often irregular, enlargement of the attached and marginal gingiva due to several causes (Fig 1), such as drugs (anticonvulsants, cyclosporine, calcium channel blockers, erythromycin), infections and autoimmune hormonal changes (pregnancy, puberty), nutritional deficiencies (vitamin C, scurvy), and systemic disease (leukemia, sarcoidosis, Wegener’s granulomatosis) Localized forms probably result from an unusual hyperplastic tissue. Marginal gingiva The free gingival margin passively lies against the tooth extending coronally from the free gingival groove The inner surface (next to the tooth) of the free gingiva forms the gingival wall of the sulcus The marginal gingiva extends from the free gingival margin to the attached gingiva (Figure 2). Marginal gingiva facial or lingual surface b/w the line angles Papillary tissue tissue that is between the interdental space Diffuse Tissue marginal and papillary that extends all the way to the mucoginvial line (attached gingiva) Gingival color healthy pale coral, salmon pink.
Surgical intervention was planned, to excise the remaining hyperplastic tissue Since, the patient had a diastema between 11 and 12, a papilla preservation flap was planned, to preserve the interdental papilla and also to prevent the apical migration of marginal gingival in relation to 11, 12. Anatomical terminology The free gingival margin is the interface between the sulcular epithelium and the epithelium of the oral cavity This interface exists at the most coronal point of the gingiva, otherwise known as the crest of the marginal gingiva. Gingiva definition is gum Time Traveler for gingiva The first known use of gingiva was circa 18 See more words from the same year.
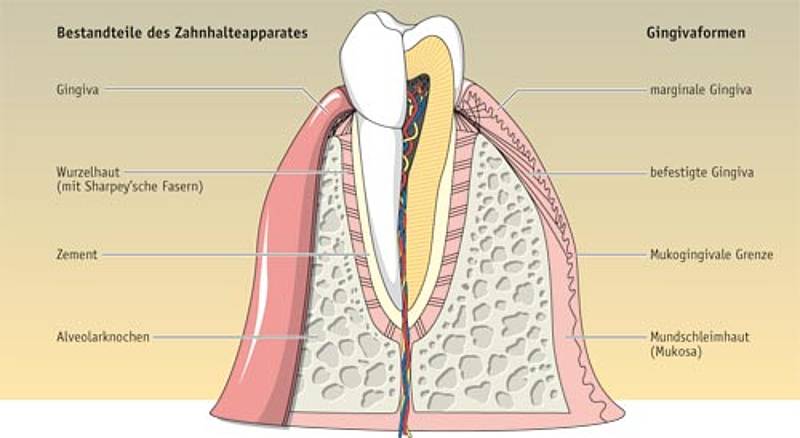
Desquamative gingivitis Desquamative gingivitis is a descriptive term, first introduced by Prinz in 1932 1) that is synonymous with the presence of erythema, desquamation, erosion, and blistering of attached and marginal gingiva, signs that represent different mucocutaneous disorders 2) Desquamative gingivitis is characterized by the erythematous gingiva, desquamation and erosion of the gingival epithelium, and blister formation 3). Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen, red, and may bleed In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. GINGIVA “Gingiva is the part of the oral mucosa that covers the alveolar processes of the jaws and surrounds the neck of the teeth (Carranza 1o th ed) ““The fibrous investing tissue, covered by keratinized epithelium, which immediately surrounds a tooth and is contiguous with its periodontal ligament and with the mucosal tissues of the mouth””.
Stippling of Gingiva Healthy gingiva presents a textured surface like that seen on the surface of an Orange Peel which is called as StippledIt is also called as Alternate protuberances & depressions on gingival surface Stippling was thought to indicate good gingival health, but it has since been shown that smooth gingiva is not an indication of disease, unless it is smooth due to loss of. AAP members are invited to post comments on terms by clicking on the term and using the comment feature at the bottom of the definition The InService Examination Committee will review comments to identify terms that need to be updated and those updates will be posted to the Glossary. The marginal gingiva is stabilized by the gingival fibers that have no bony support The gingival margin, or free gingival crest, at the most superficial part of the marginal gingiva, is also easily seen clinically, and its location should be recorded on a patient's chart Attached gum The attached gums are continuous with the marginal gum.
Gingival of or relating to the gums Periodontal ligament shock absorber that attaches the tooth to bone Plaque Film on teeth which causes cavities, gingivitis and periodontitis Soft film deposited on the irregular surfaces of teeth;. Stippling is seen at the sites of fusion of the epithelial ridges or Rete Pegs and corresponds to the fusion of the valleys created by the connective tissue papillae. Biofilm forms at the gingival margin of the sinus tract and leads to marginal periodontitis When plaque or calculus is encountered upon probing, the treatment and prognosis of the tooth are altered;.
Marginal Gingiva Sulcus depth greater Free gingival margin thicker and rounder (due to cervical constriction of primary teeth) Flaccid and retractable immature connective tissue, immature gingival fiber system, increased vascularization Attached gingiva Appears less dense and redder thinner, less keratinized epithelium. Contains food debris, bacteria, bacteria byproducts, saliva and salivary enzymes. Gingiva is a part of the oral mucosa lining the alveolar process of jaws and surrounds the teeth to provide a seal around them It plays a major rule to faci.
Definition According to Marginal Gingiva 1) The marginal or unattached gingiva is the terminal edge or border of the gingiva surrounding the teeth like a collar 3 2) In about 50% of cases. Stabilize the marginal gingiva by connecting it with both the tissue of the more rigid attached gingiva and the cementum layer of the tooth;. Almost insufficient marginal subsistence;.
Probing depths do not take into consideration gingival recession, overgrowth or changes of the marginal gingiva associated with tissue swelling Advertisement It would be much more helpful to have a measurement of the dentogingival complex which, is the sum of all supracrestal soft tissue components and reflects the histomorphological aspect of. The mucous membrane surrounding the teeth sockets Explanation of marginal gingiva Marginal gingiva Article about marginal gingiva by The Free Dictionary https//encyclopedia2thefreedictionarycom/marginalgingiva. Also called the free margin gingiva, forming the gingival sulcus space between the tooth and attached gingival measuring approximately 1 to 3 mm in depth.
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen, red, and may bleed In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Marginal gingiva The crest of the free gingiva surrounding the tooth like a collar It is about 1 mm wide and forms the soft tissue portion of the gingival sulcus. The tooth now requires both endodontic and periodontal treatments.
Definition Gingival recession is defined as the displacement of the gingival margin apical to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) It is characterized by the loss of the periodontal connective tissue fibres along the root cementum and by concomitant loss of alveolar bone The causes of gingival recession include. Gingival hyperplasia is a localized or generalized, often irregular, enlargement of the attached and marginal gingiva due to several causes (Fig 1), such as drugs (anticonvulsants, cyclosporine, calcium channel blockers, erythromycin), infections and autoimmune hormonal changes (pregnancy, puberty), nutritional deficiencies (vitamin C, scurvy), and systemic disease (leukemia, sarcoidosis, Wegener’s granulomatosis) Localized forms probably result from an unusual hyperplastic tissue. The gingiva is palpated with a blunt instrument to check for its consistency The gingival connective tissue is composed of collagen fibers and is firmly bound to the underlying mucoperiosteum, giving it a firm and resilient consistency During gingival inflammation, the gingival consistency becomes soft and edematous.
When mucositis is left untreated the infection involves the tissue under the marginal gingiva and the surface of the implant that offers bacteria the way to reach the alveolar bone which starts to reabsorb / recede In case of severe periimplantitis it is difficult to reverse the pathology and surgical or laser treatment are often required.

Zahnfleisch Wikipedia

Anatomiske Strukturer Flashcards Quizlet

Praeparat 53 Fri Marginal Gingiva Laengdesnit Af Fri Marginal Gingiva Diagram Quizlet
Marginale Gingiva Definition のギャラリー

Dental Tribune International

Anatomy Of The Periodontium Image Collections Human Body Anatomy

Repeatability Of Ultrasonic Determination Of Gingival Thickness Request Pdf
Zahnfleisch Gingiva Med Kom

Candidatus Rickettsia Tarasevichiae Infection In Eastern Central China A Case Series Annals Of Internal Medicine Vol 164 No 10

Usb2 Dental Appliance Having Ornamental Design Google Patents

Rot Weisse Asthetik Wir In Der Praxis De

Color Atlas Of Dental Medicine Aesthetic Dentistry Pages 251 300 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
Anatomy Of The Periodontium Image Collections Human Body Anatomy
Zahnhalteapparat

Gingiva Doccheck Flexikon

Fixed Prosthesis With Vertical Margin Closure Ezio Bruna Pdf Dental Implant Periodontology

Pdf The Important Considerations And The Clinical Assessment Proceeding Crown Lengthening Surgery Revisited Review

Pdf The Influence Of Margins Of Restorations On The Periodontal Tissues Over 26 Years Filling Margin And Periodontal Condition
Macroscopic Features Of Gingiva

Anatomiske Strukturer Flashcards Quizlet

Virtually Representing An Orthodontic Treatment Outcome Using Automated Detection Of Facial And Dental Reference Objects Patent Grant Pokotilov Et Al Sep Align Technology Inc

Usb2 Dental Appliance Having Ornamental Design Google Patents

System And Method For Manufacturing A Dental Prosthesis And A Dental Prosthesis Manufactured Thereby Patent Grant Kopelman Et Al Sept Align Technology Inc

Jos European Journal Of Oral Surgery By Ariesdue Srl Issuu
Macroscopic Features Of Gingiva
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4679/AZAvsgaHNN88XCgxtEhBeA_Gum_01.png)
Gingiva Types Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4681/2xL9HTqyI44LBnu7WRA_stratified_squamous_keratinizing_epithelium02.png)
Gingiva Types Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub

Die Rote Asthetik Zwp Online Das Nachrichtenportal Fur Die Dentalbranche

Anatomie Du Parodonte Ce500 Dentalcare Ca

Universitatsklinik Fur Zahnmedizin Und Mundgesundheit Graz Atiologie Der Parodontalerkrankungen M Haas Parodontologie Und Prophylaxe Graz Pdf Free Download

Esthetic Dentistry And Ceramic Restoration 1ed Tooth Enamel Dental Composite

Gencive Wikipedia

Pdf The Influence Of Margins Of Restorations On The Periodontal Tissues Over 26 Years Filling Margin And Periodontal Condition
Diagnostikk Av Periodontale Sykdommer Den Norske Tannlegeforenings Tidende
Parodontologie Und Prophylaxe Pdf Kostenfreier Download

Grundlagen Der Parodontologie Eref Thieme

Usb2 Dental Appliance Having Ornamental Design Google Patents
Zahnfleisch Gingiva Med Kom

Giuliabonarini Dds Rdh Posts Facebook

Akut Nekrotiserende Gingivitis Tandogmund Dk

Chapter 3 Anatomy Structure And Function Of The Periodontium Dentistrykey

Mikroskopische Anatomie Des Marginale Eref Thieme

Color Atlas Of Dental Medicine Aesthetic Dentistry Pages 251 300 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Cad Cam Technology And Zirconium Oxide With Feather Edge

Parodontologie Summary Paradont Studocu

Gegen Marginale Parodontitis Kombinationsbehandlung Mit Chlorhexidin Und Laserlicht Fachgebiete Zmk Aktuell De

Chapter 3 Anatomy Structure And Function Of The Periodontium Dentistrykey
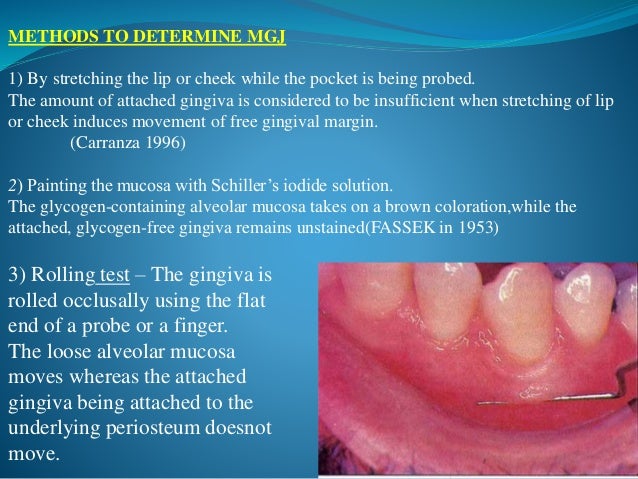
Macroscopic Features Of Gingiva
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4680/KAU7J26FqiSljZhPP7oEDA_Cervix_dentis_02.png)
Gingiva Types Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub

Dental Tribune Iran



